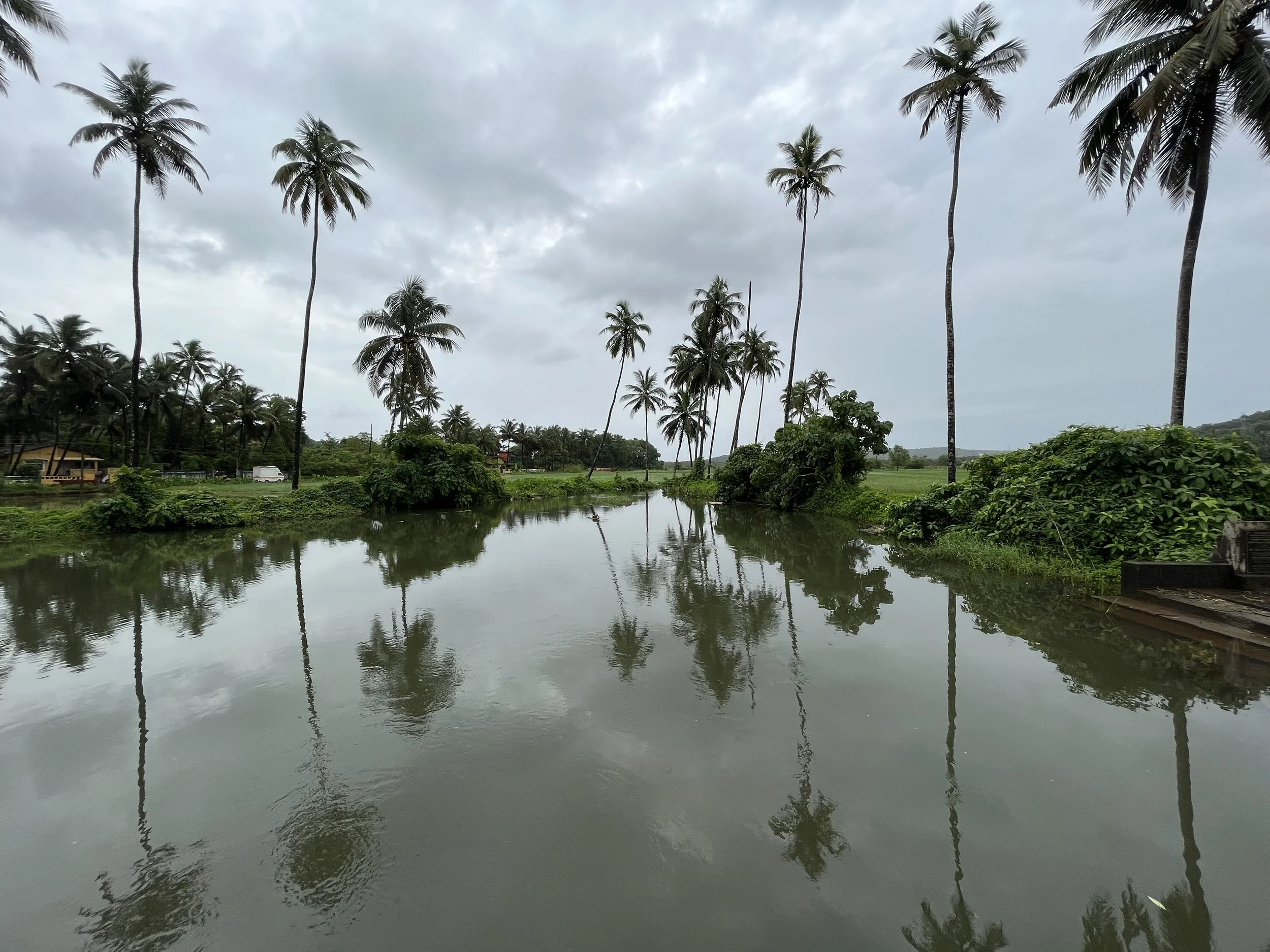
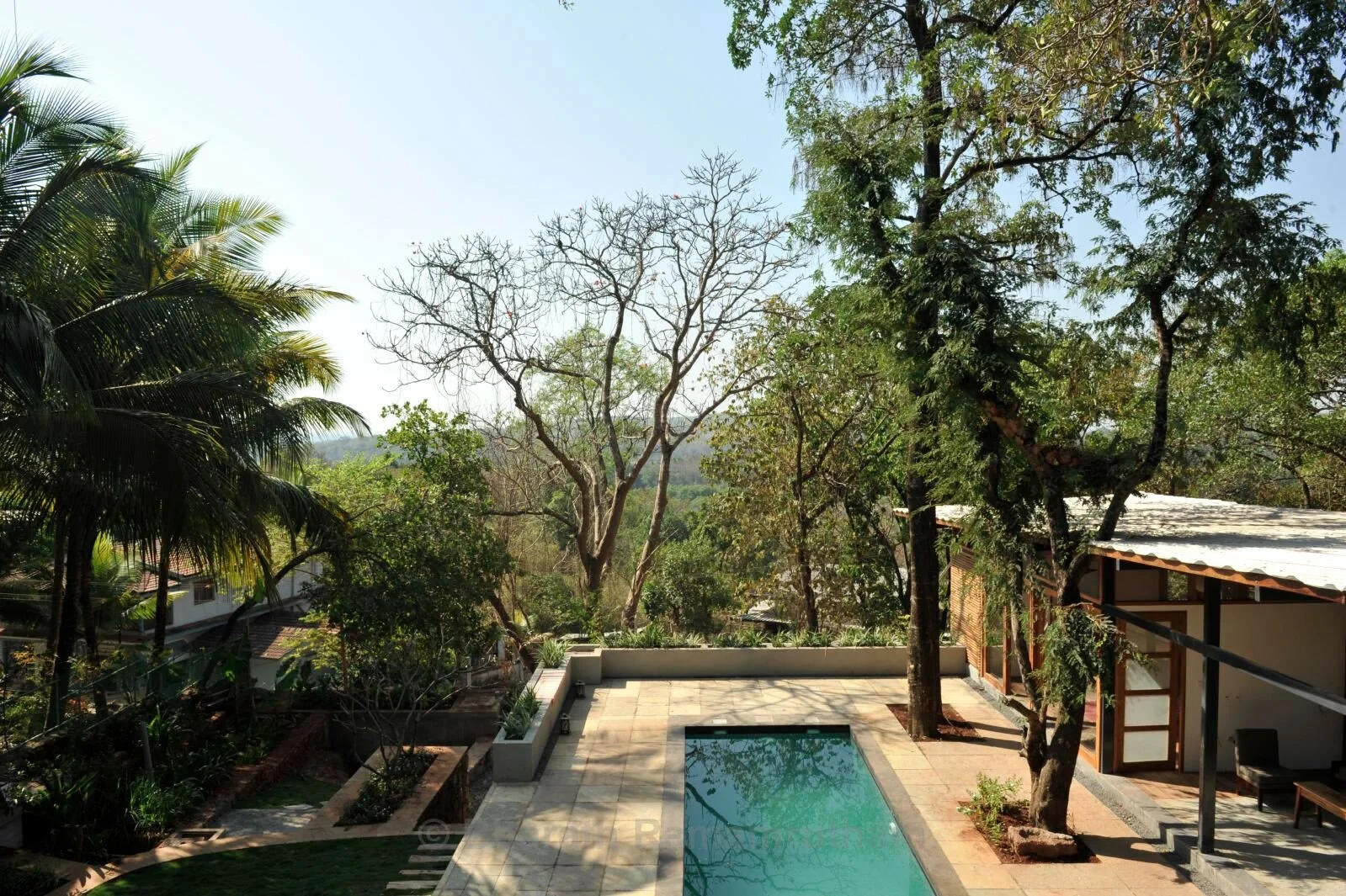
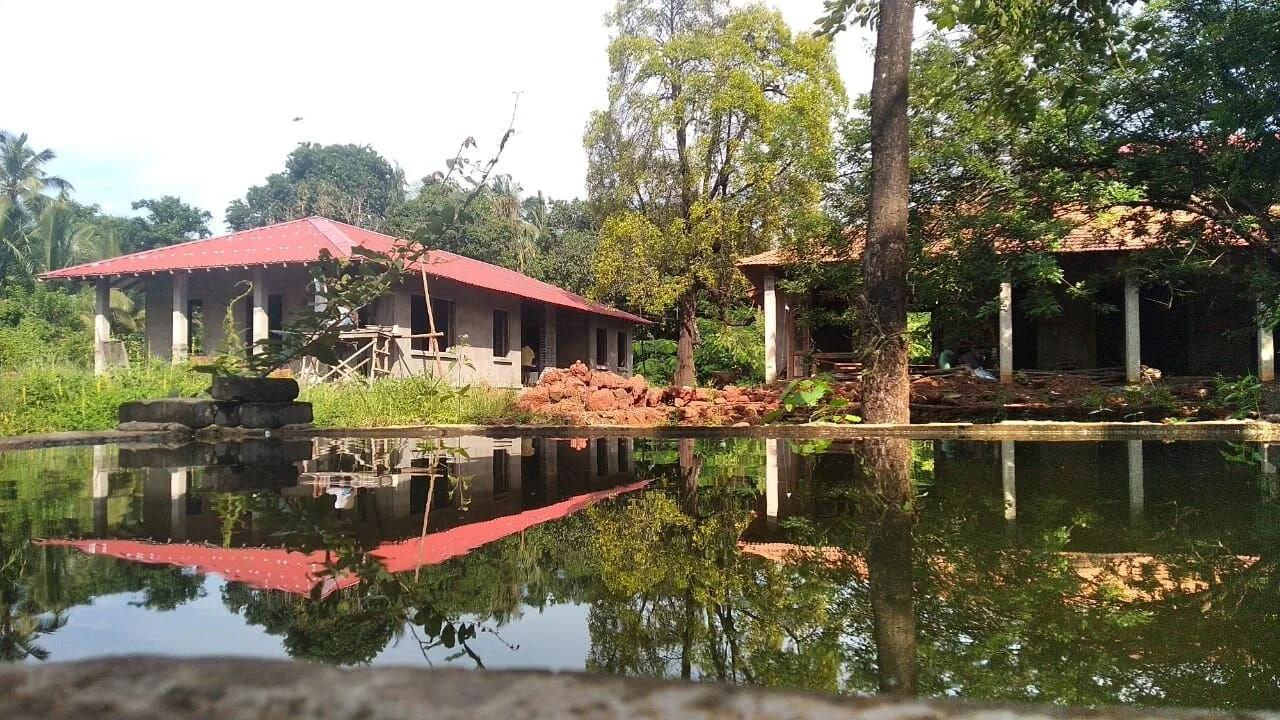
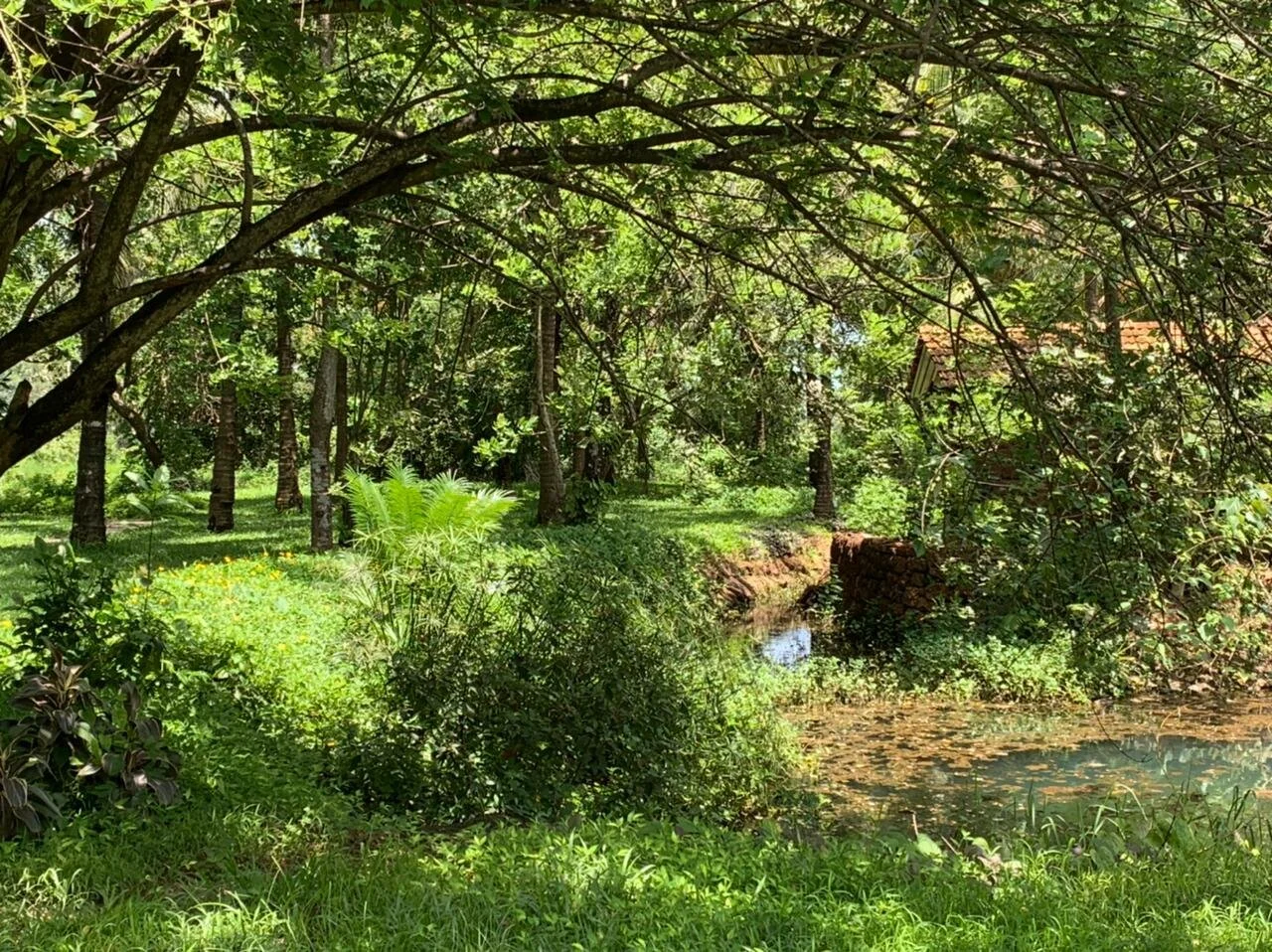
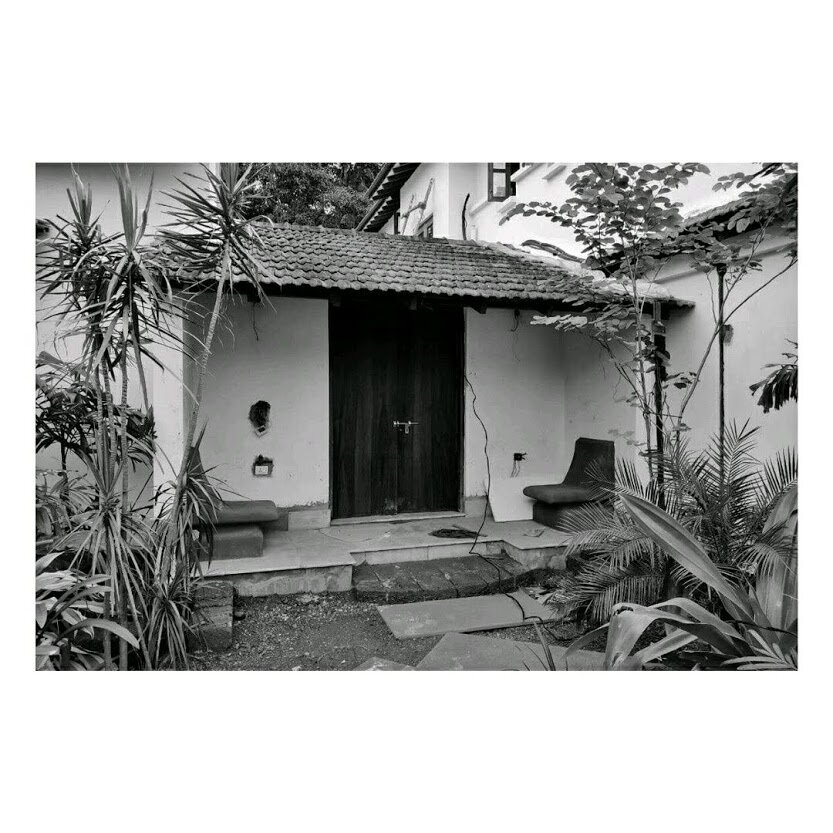
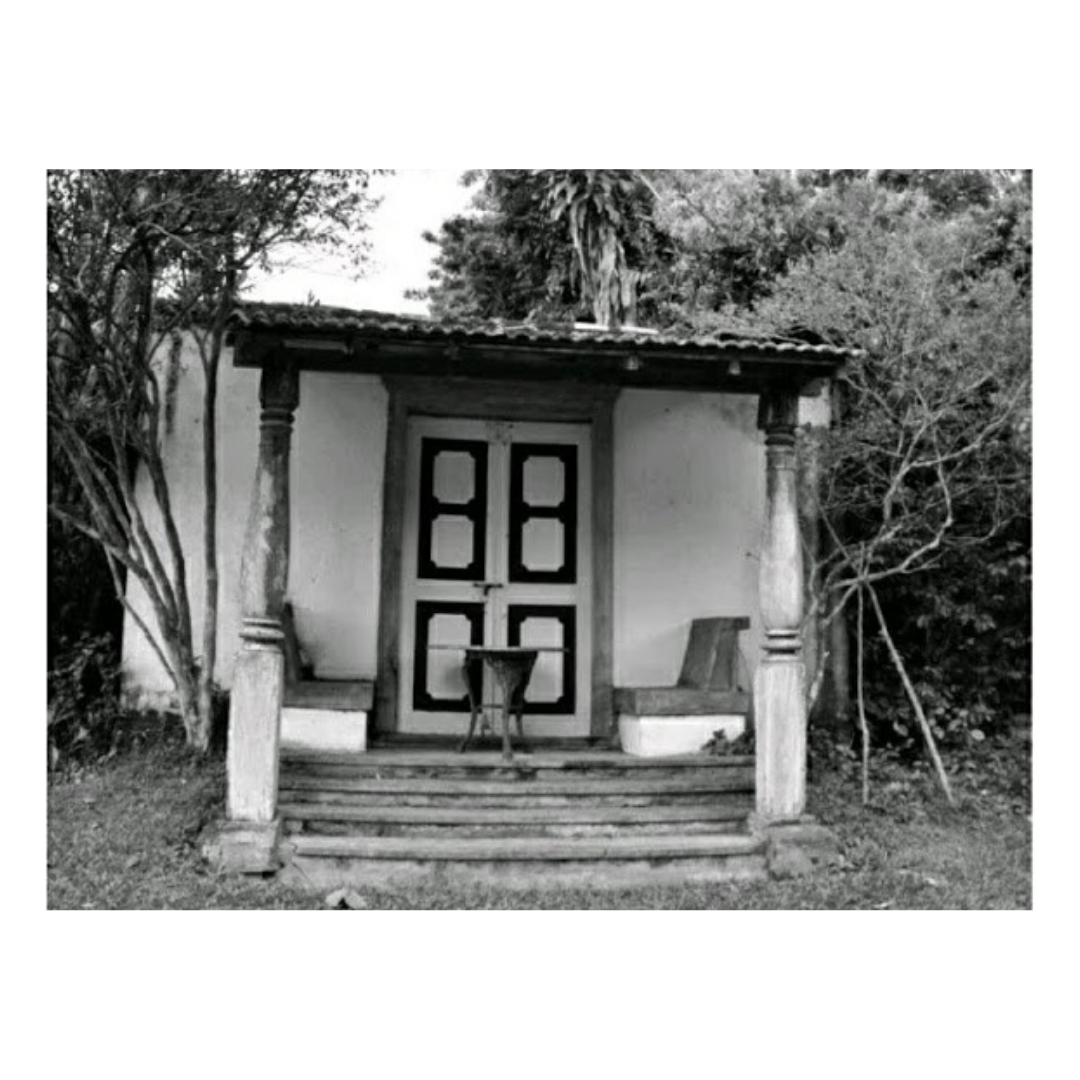
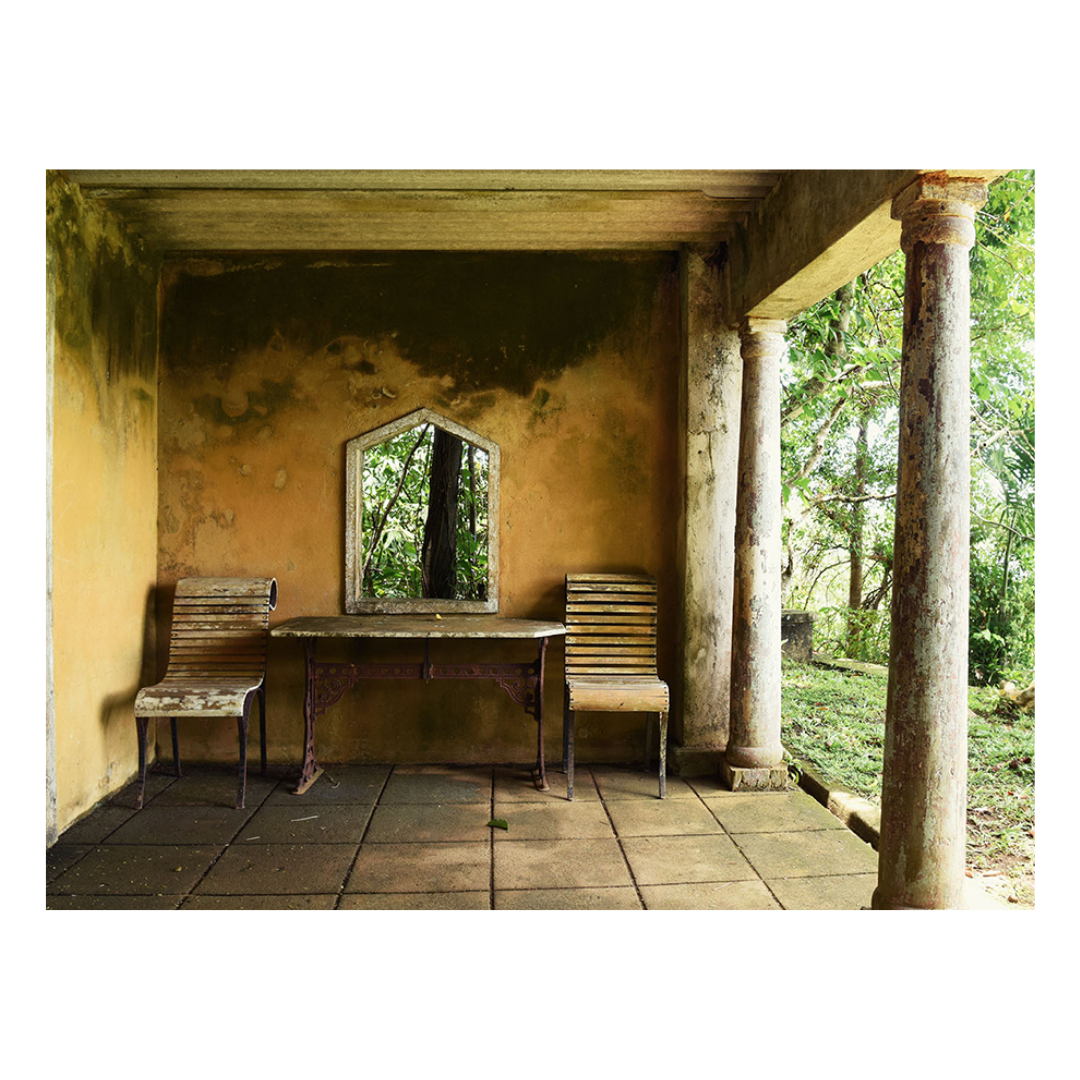
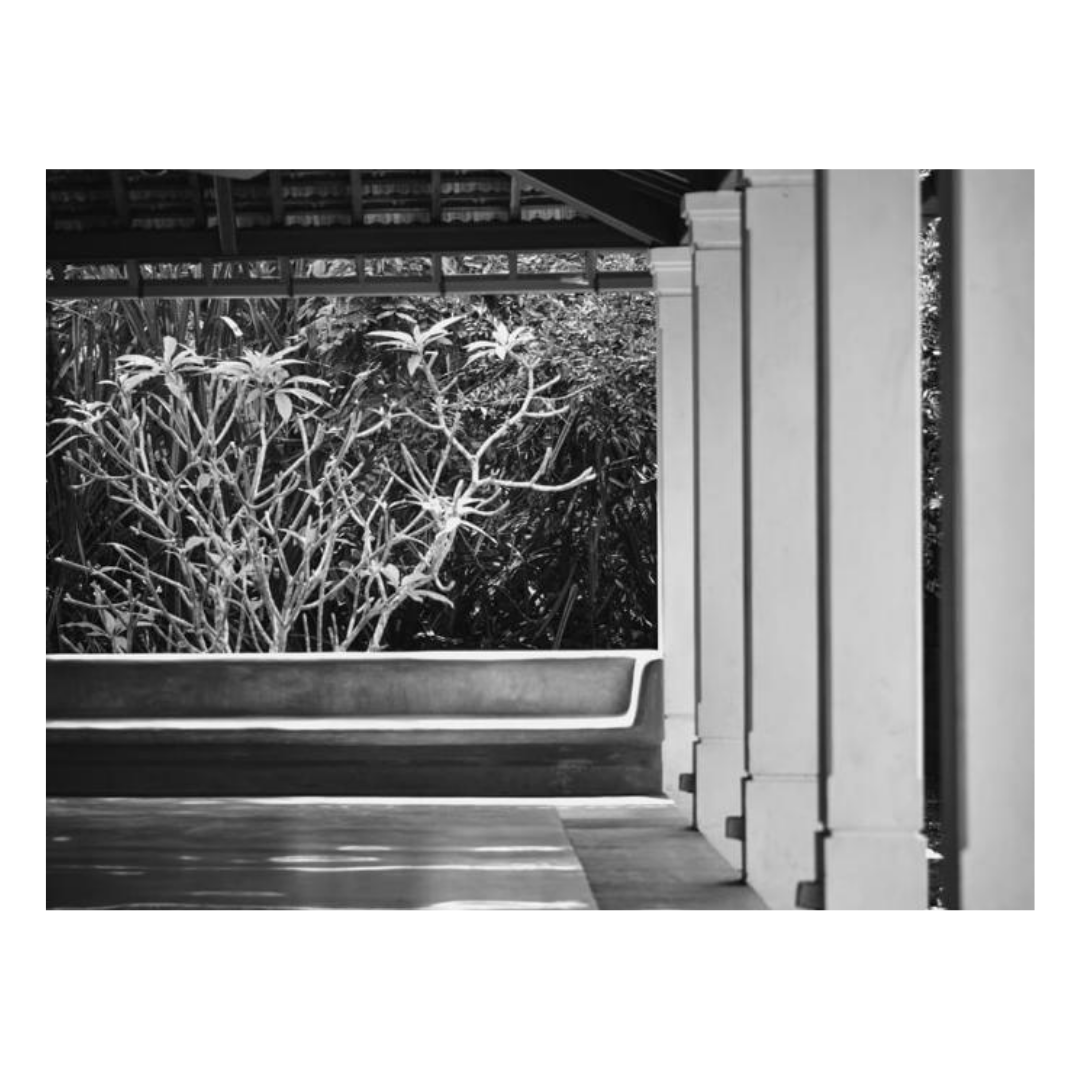
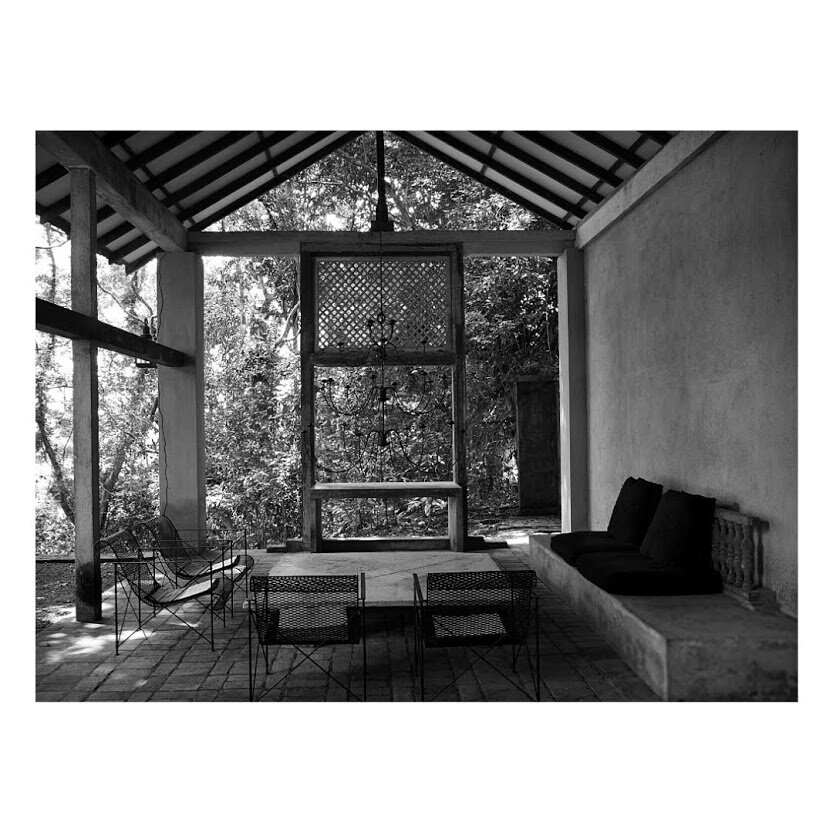
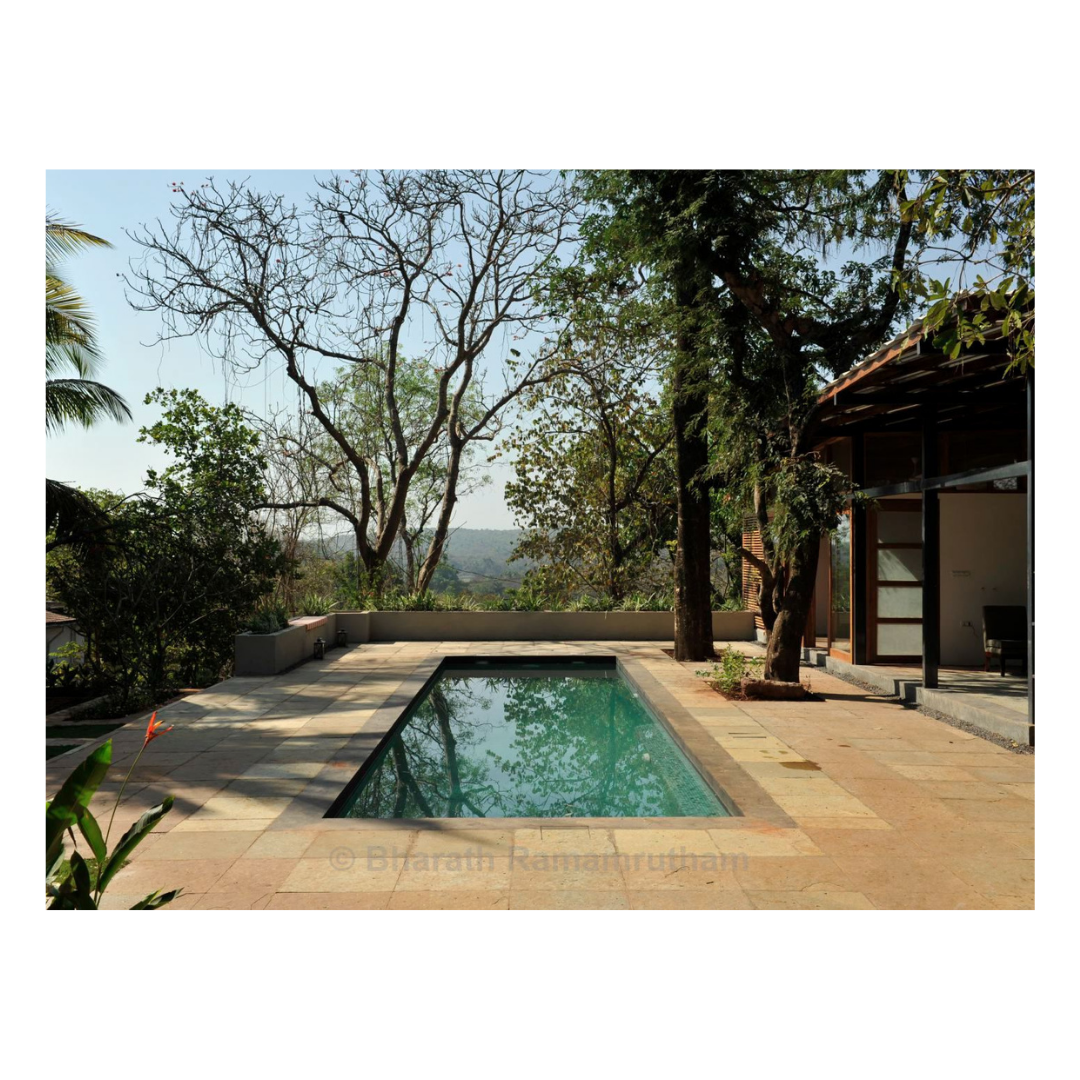
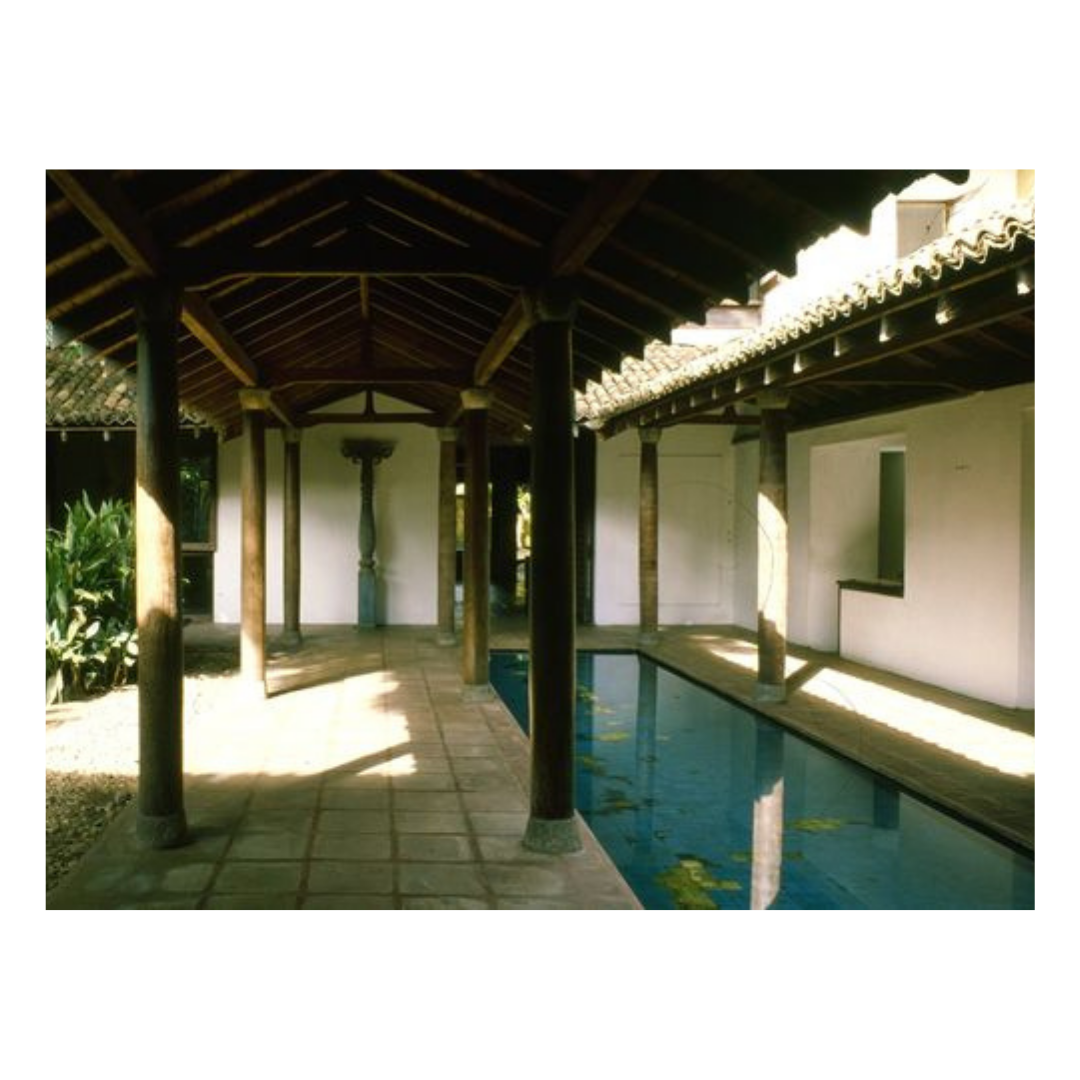
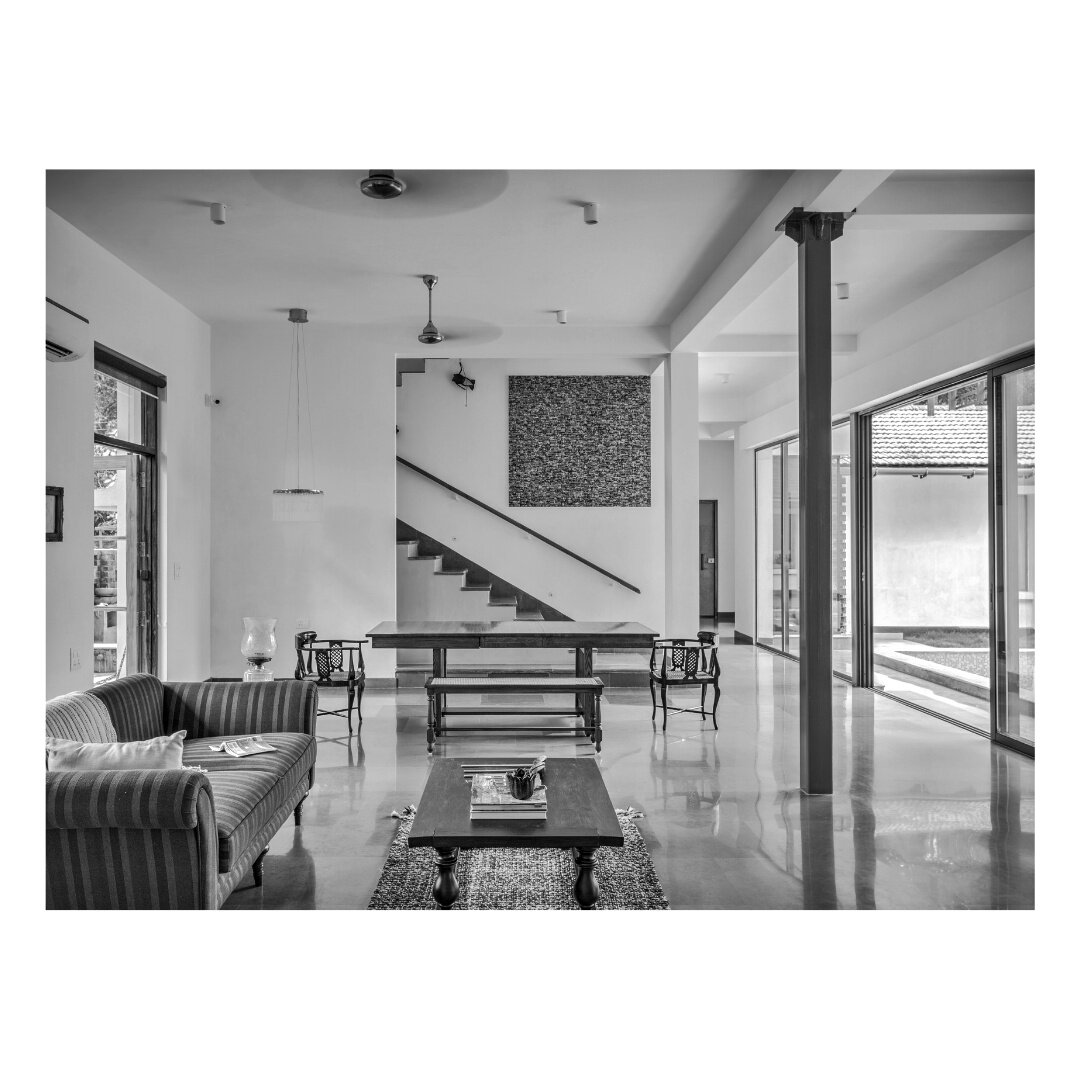
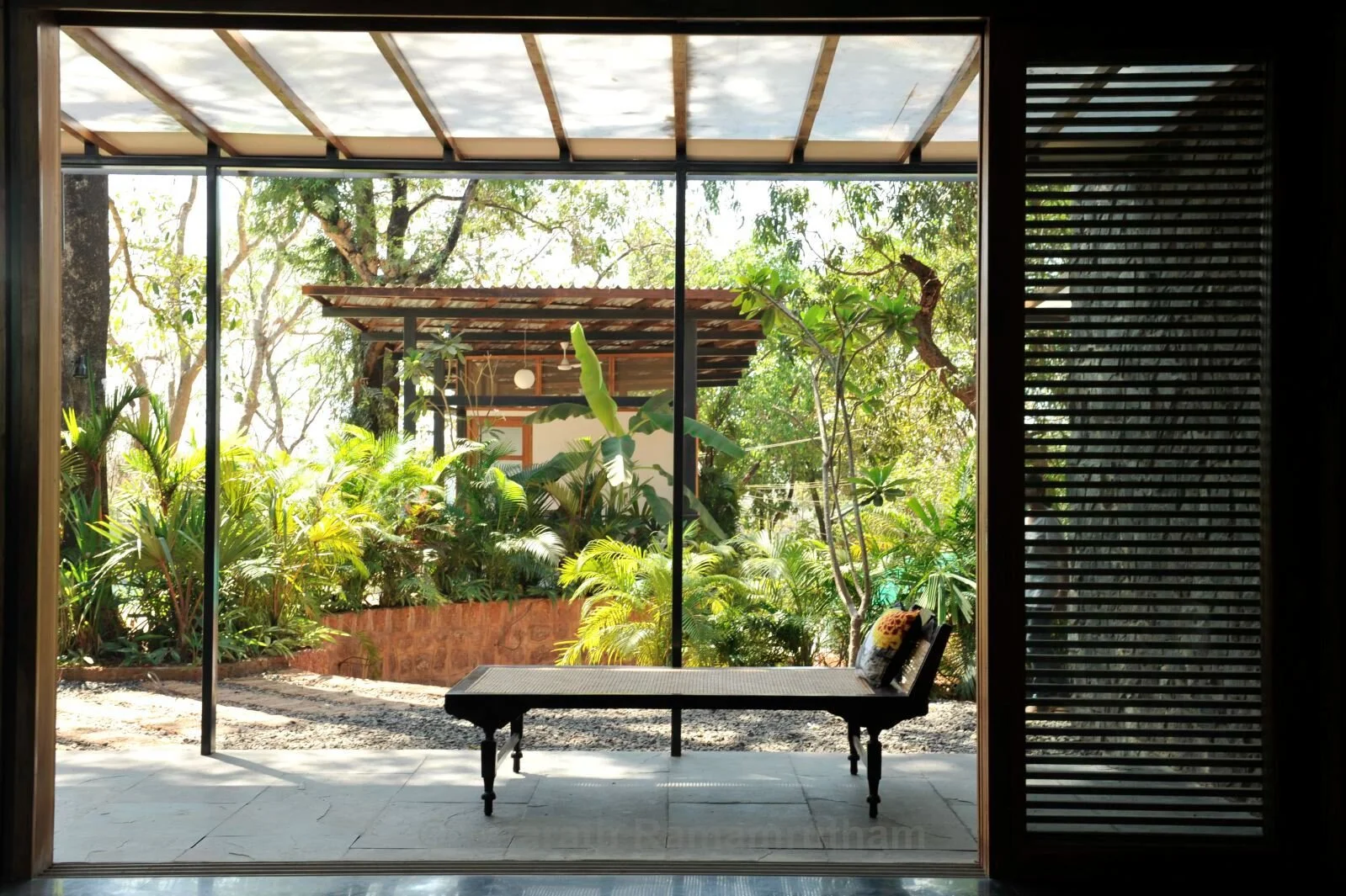
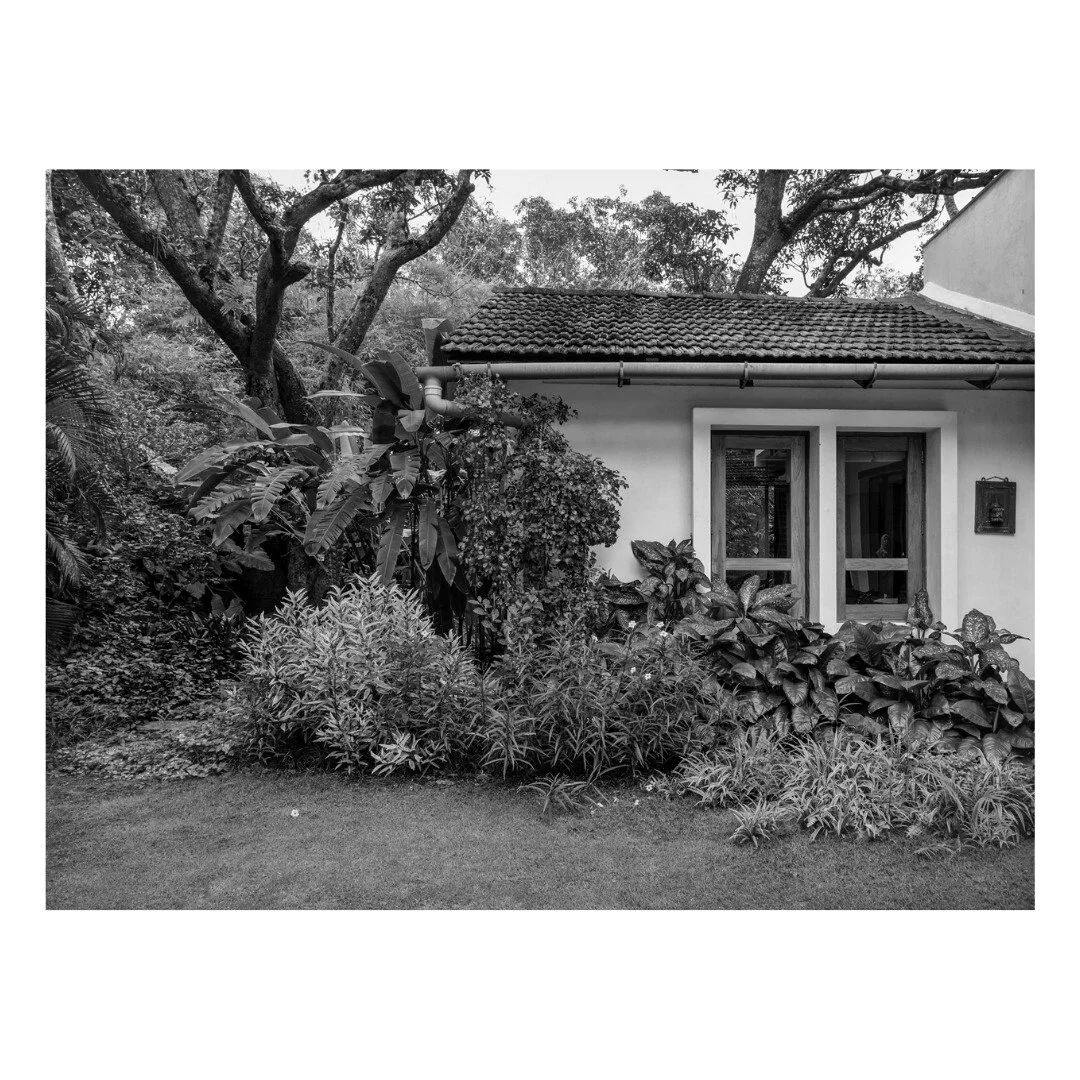
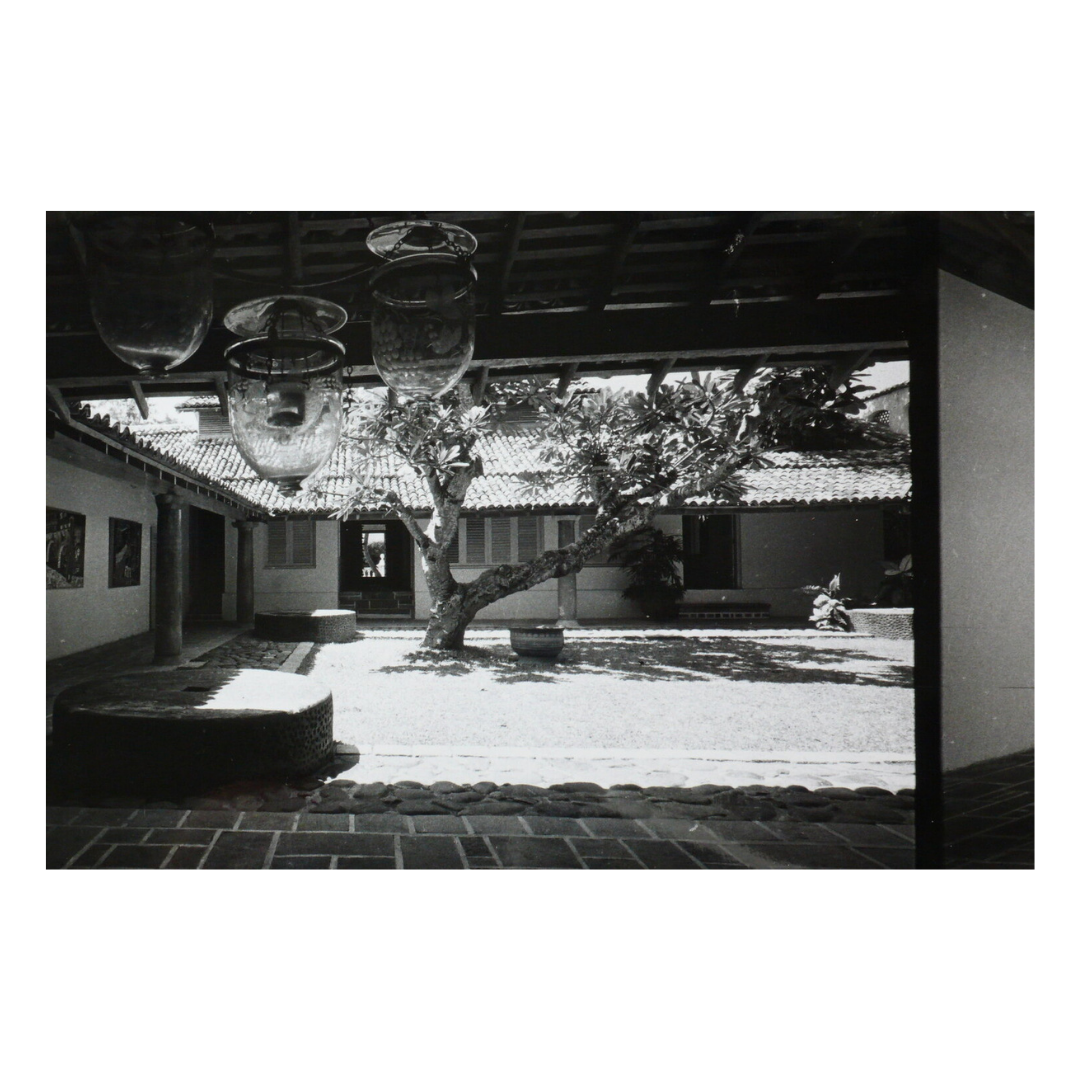
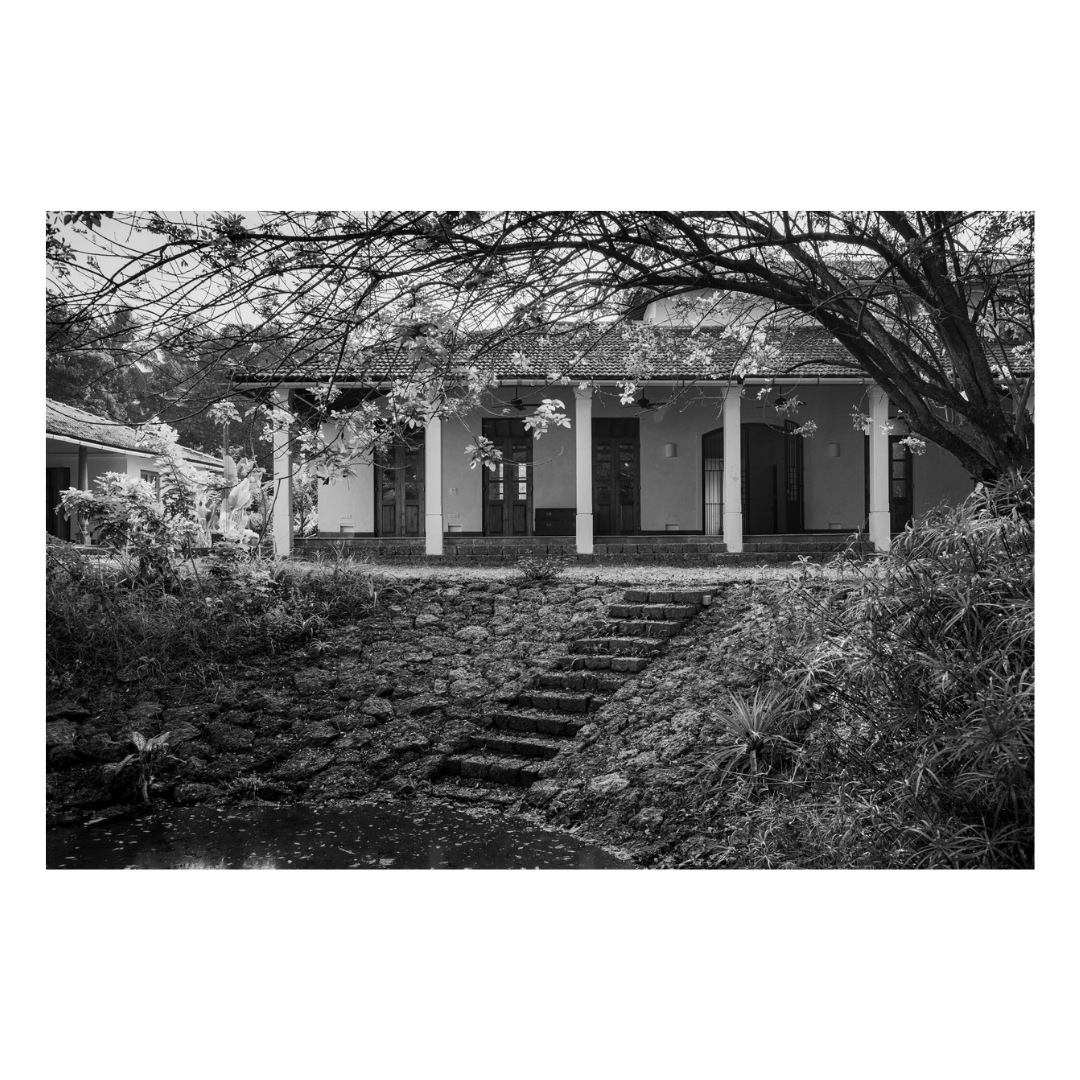
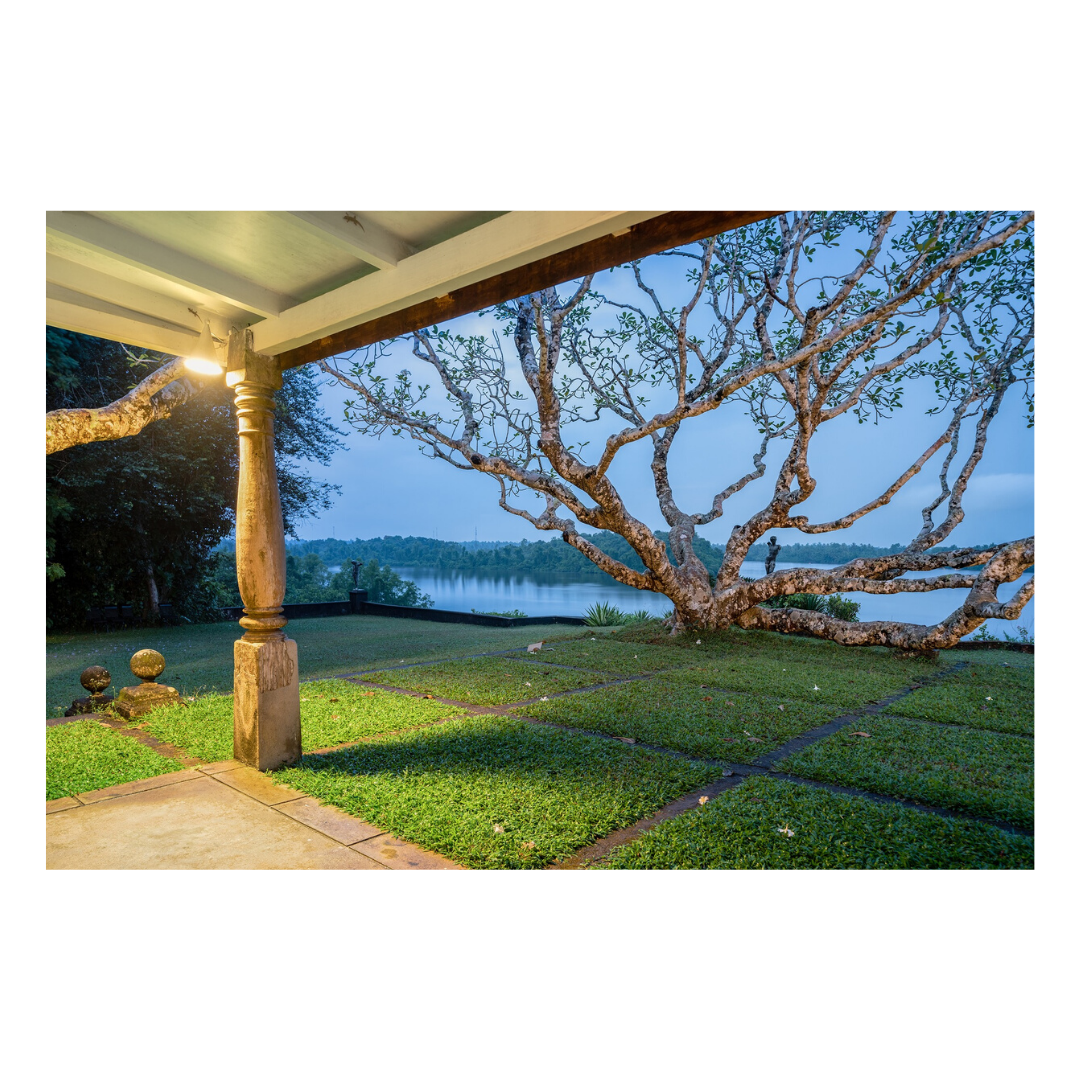
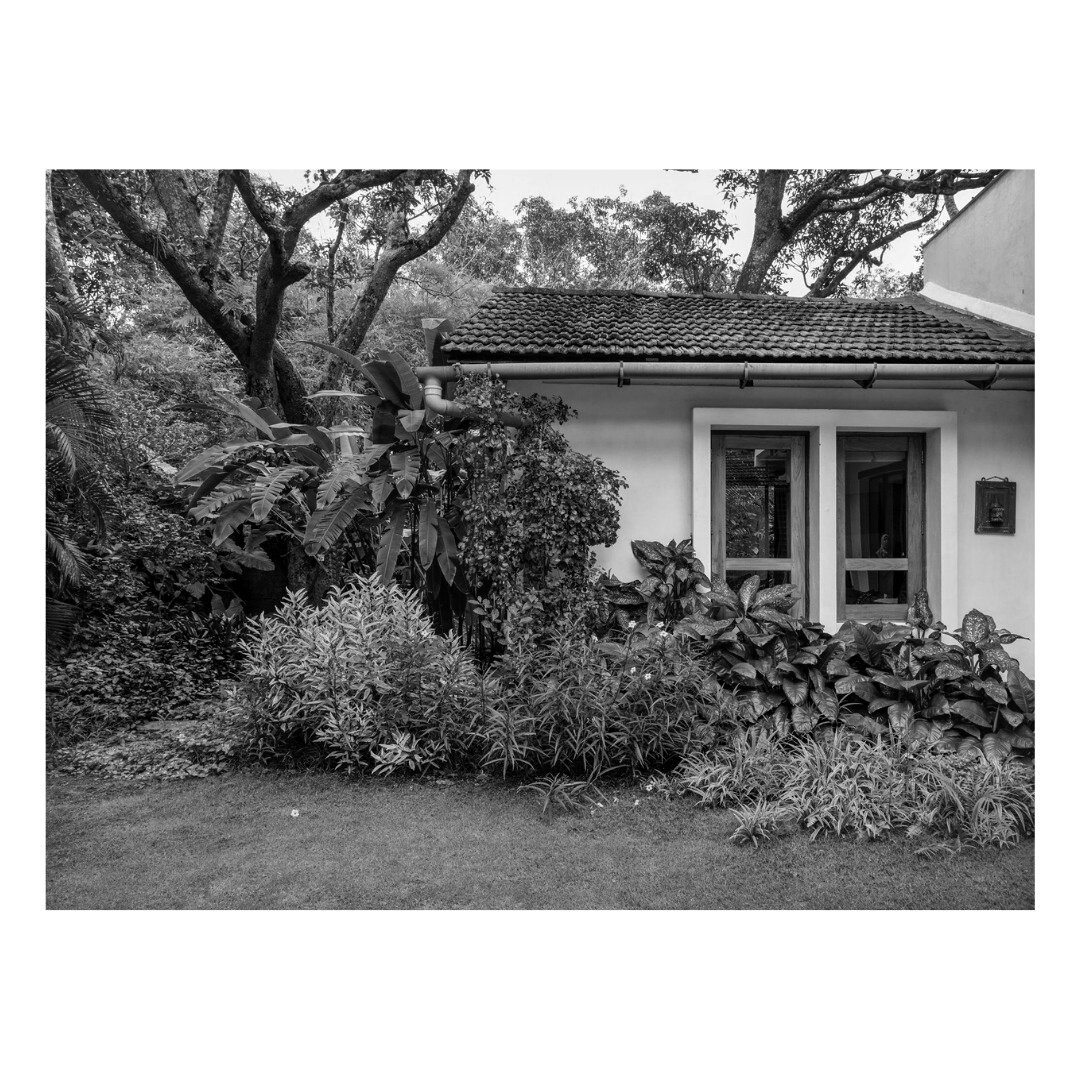
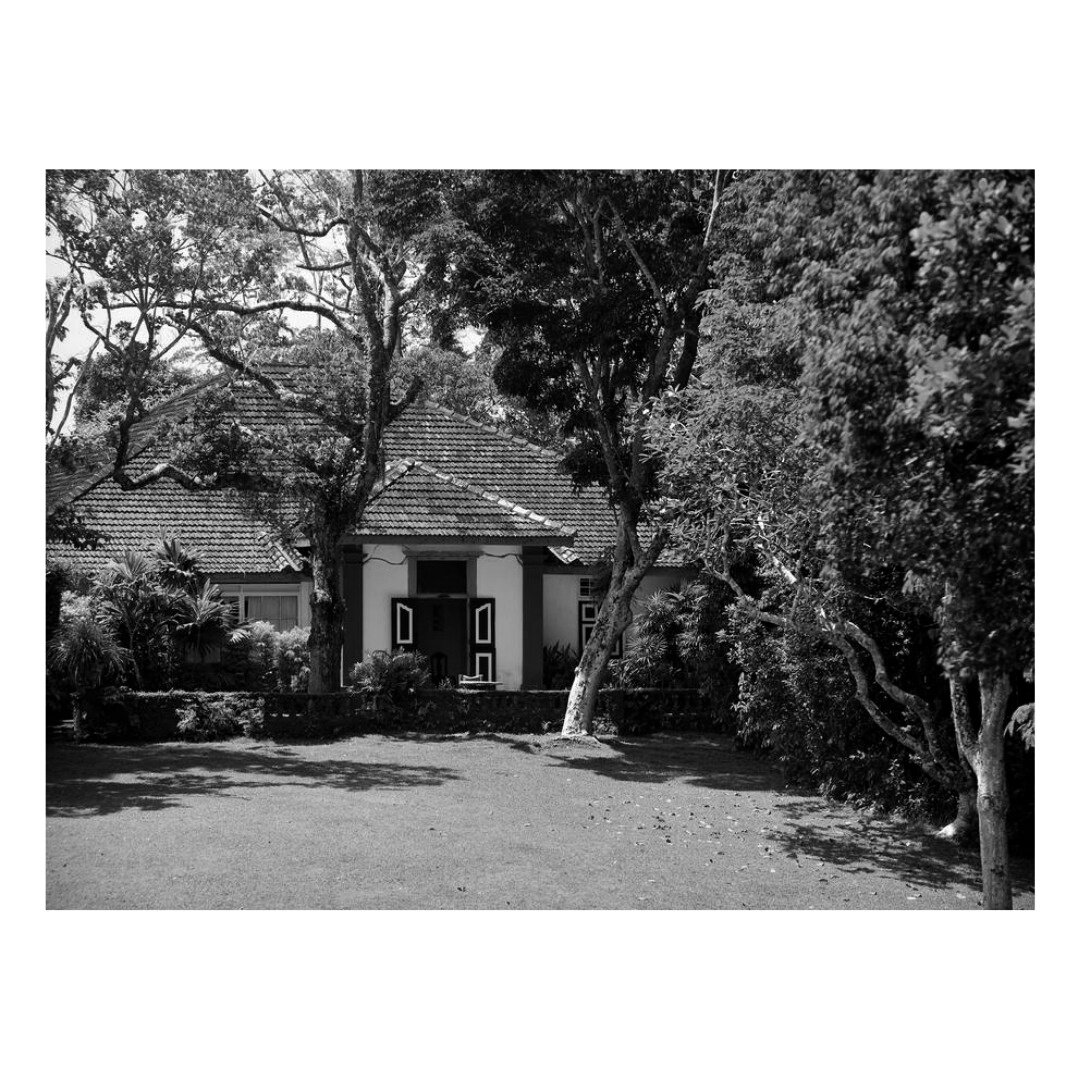
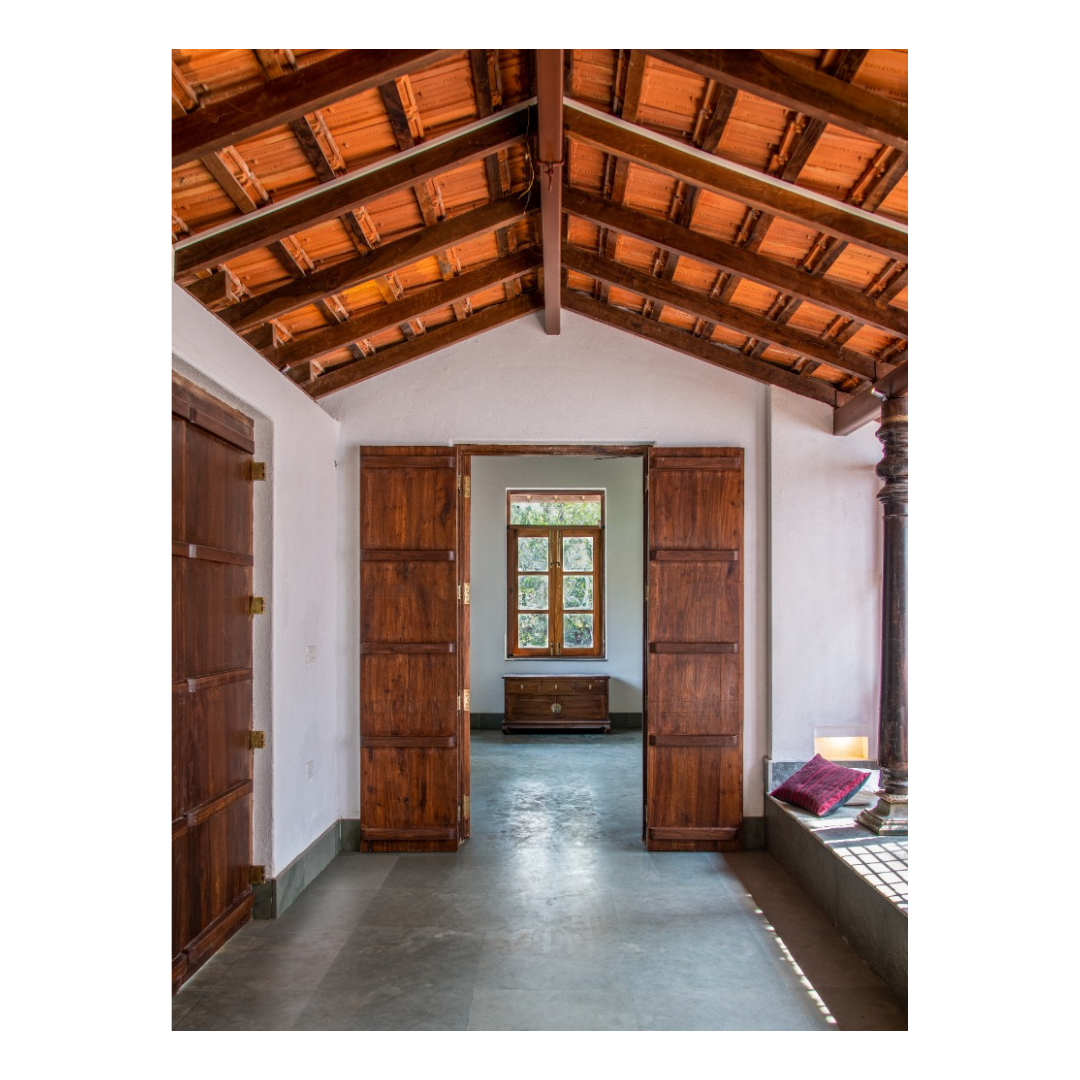
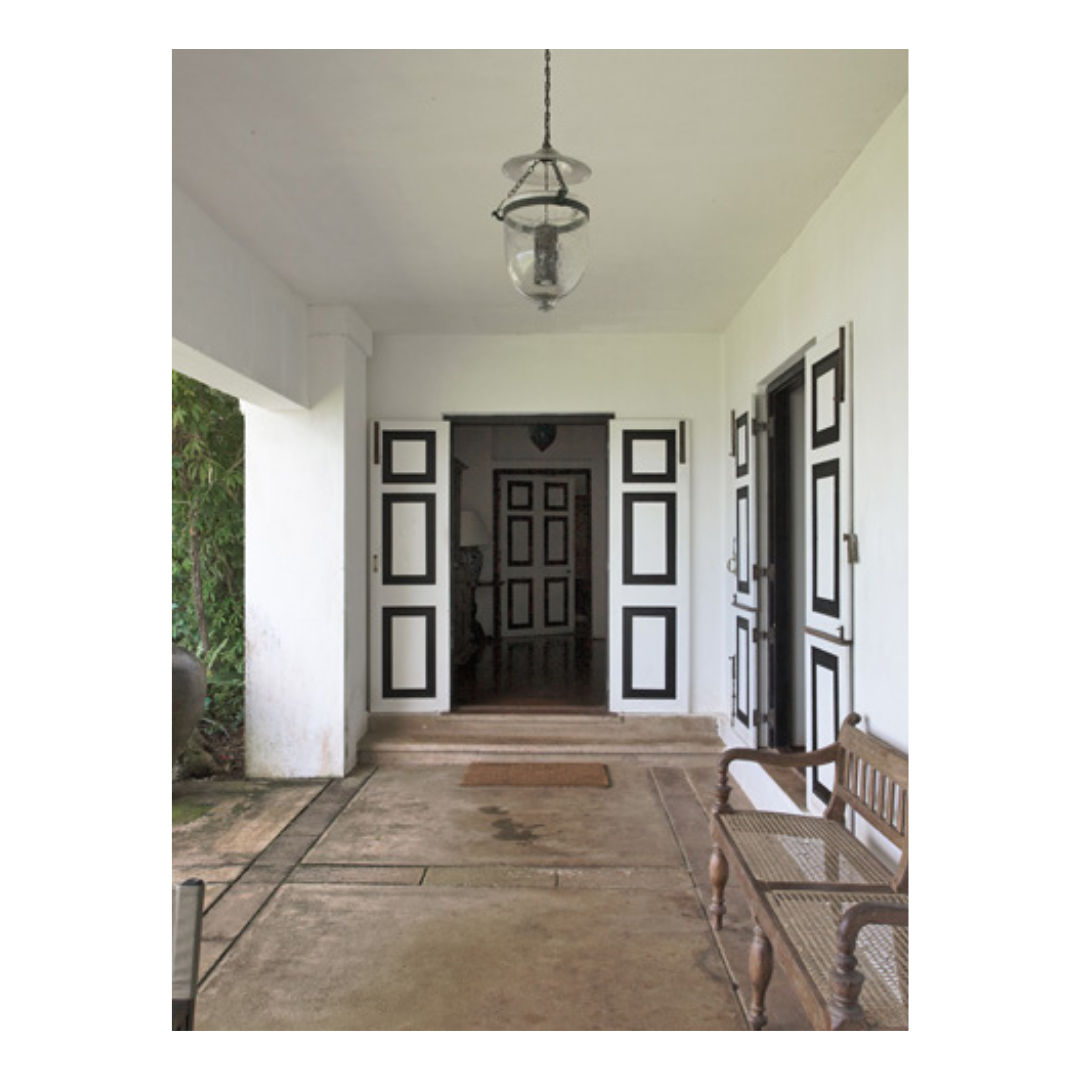
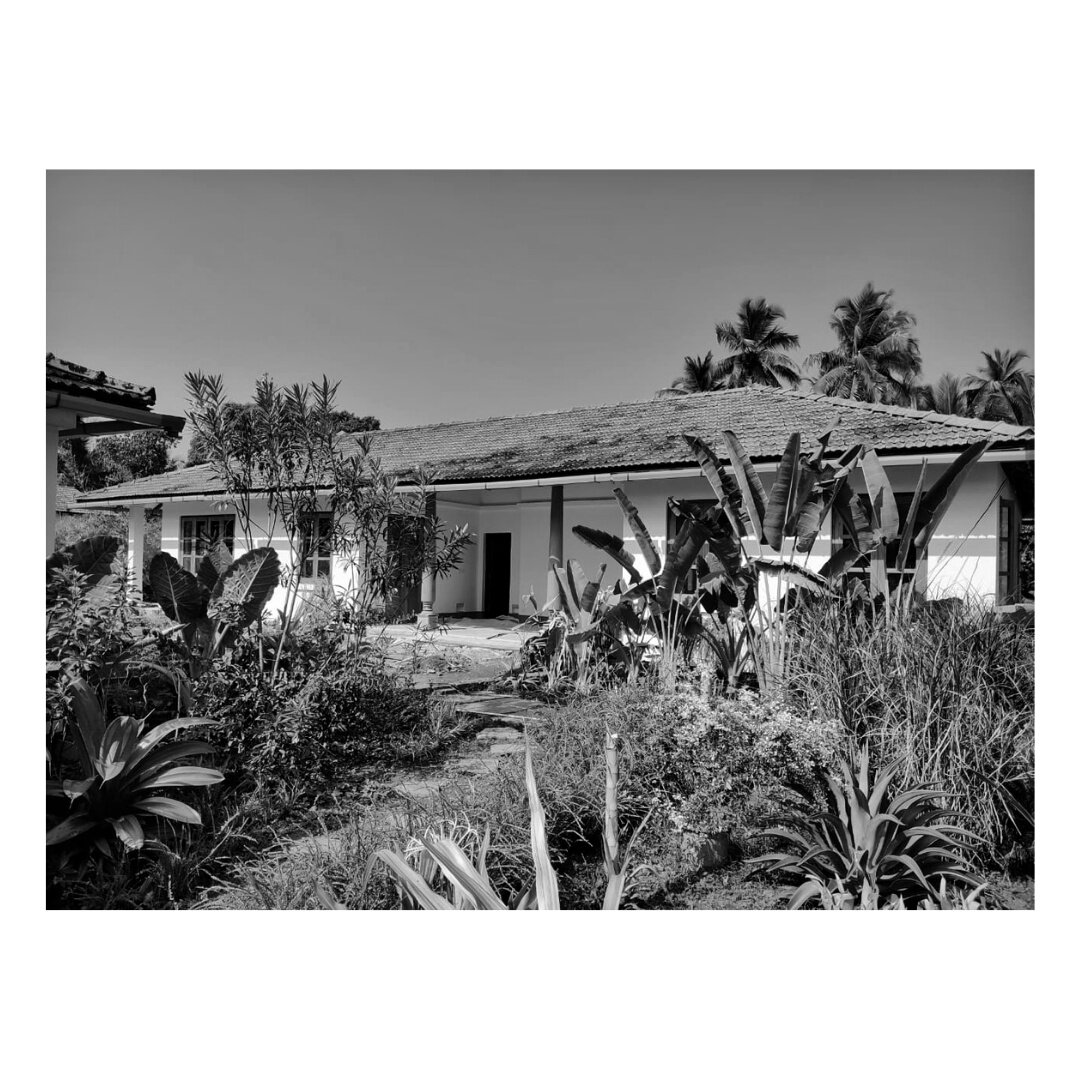
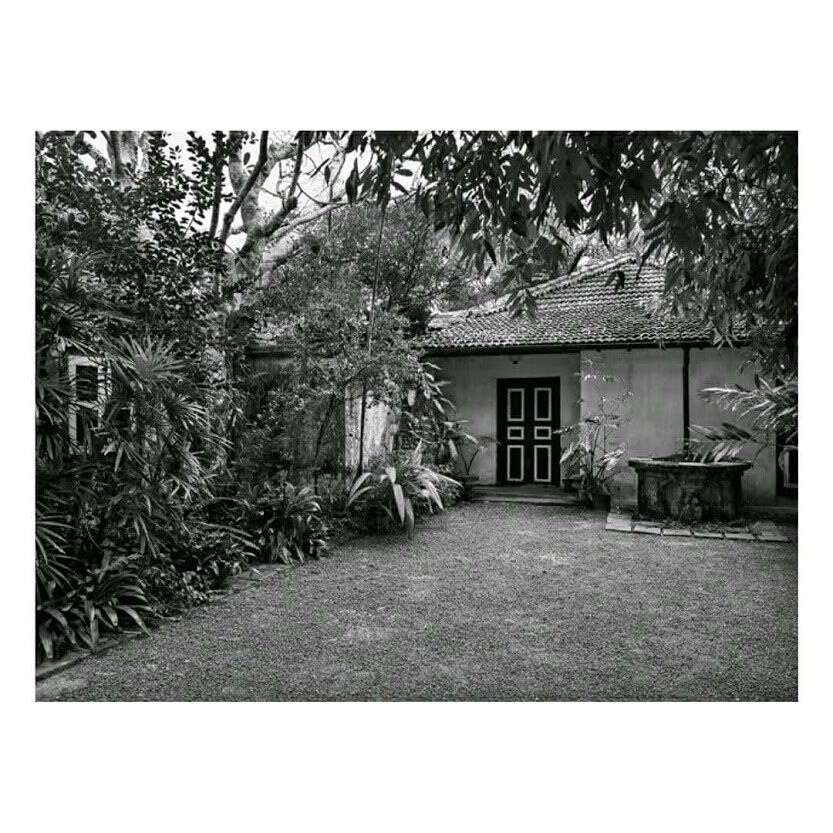
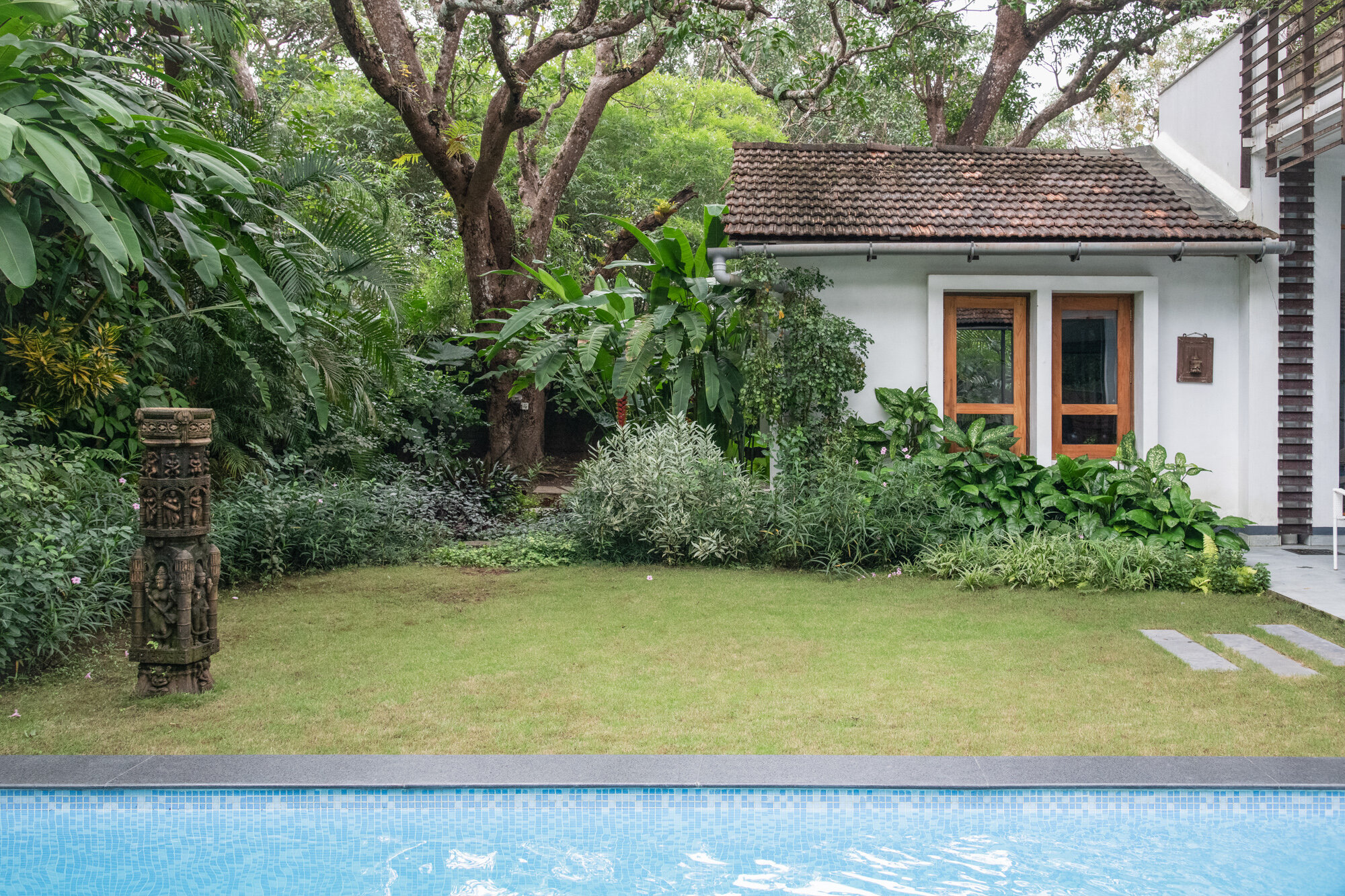
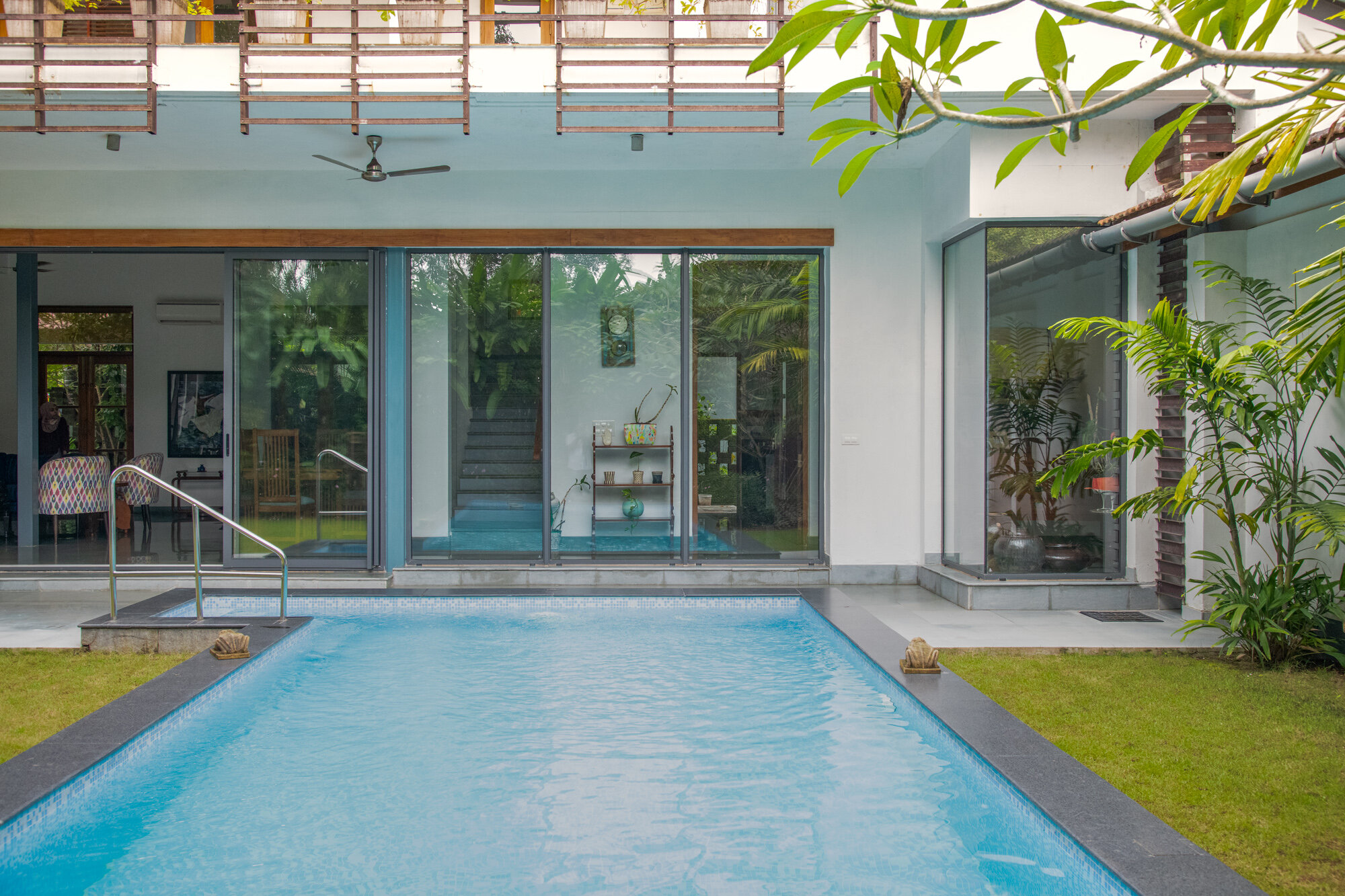
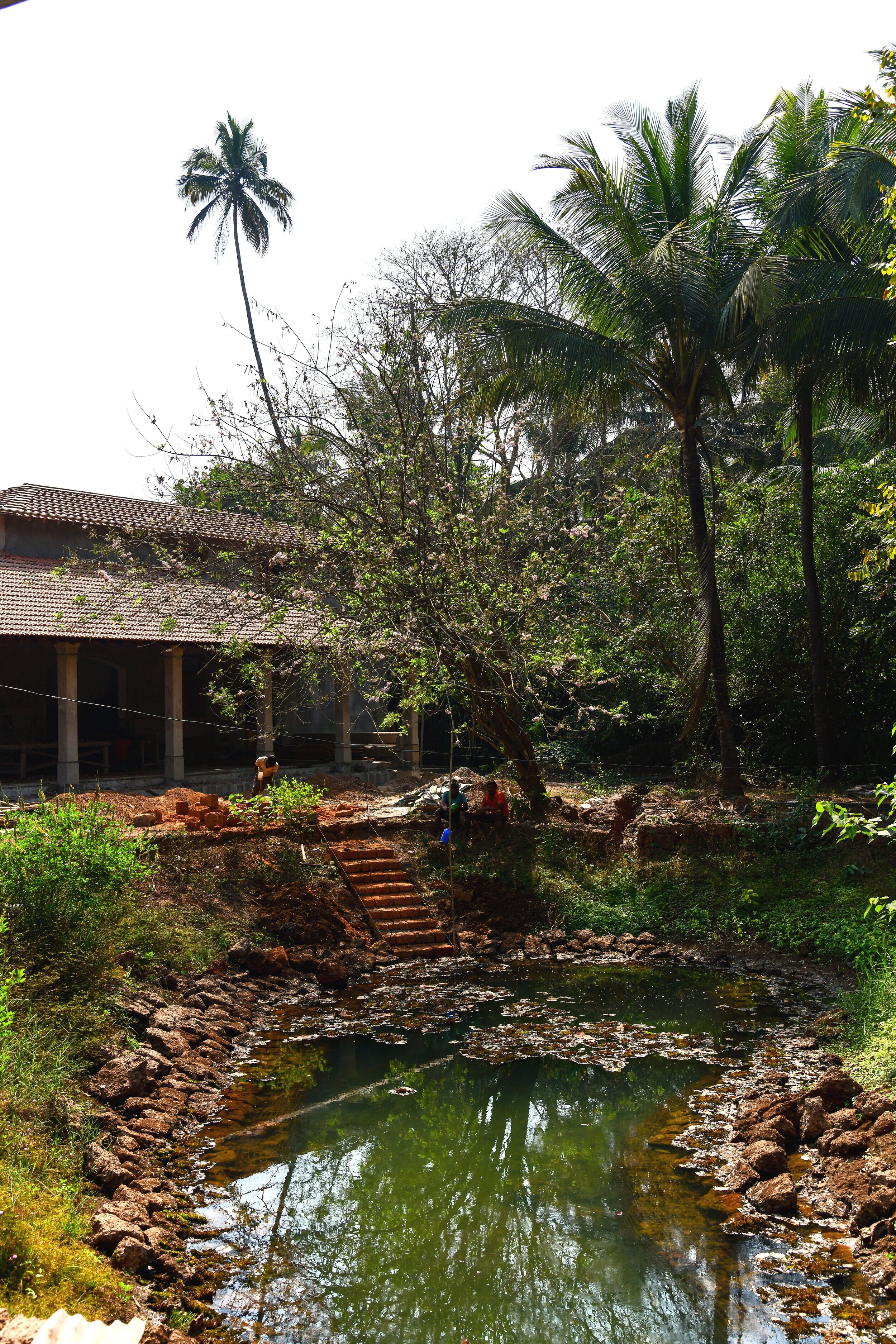
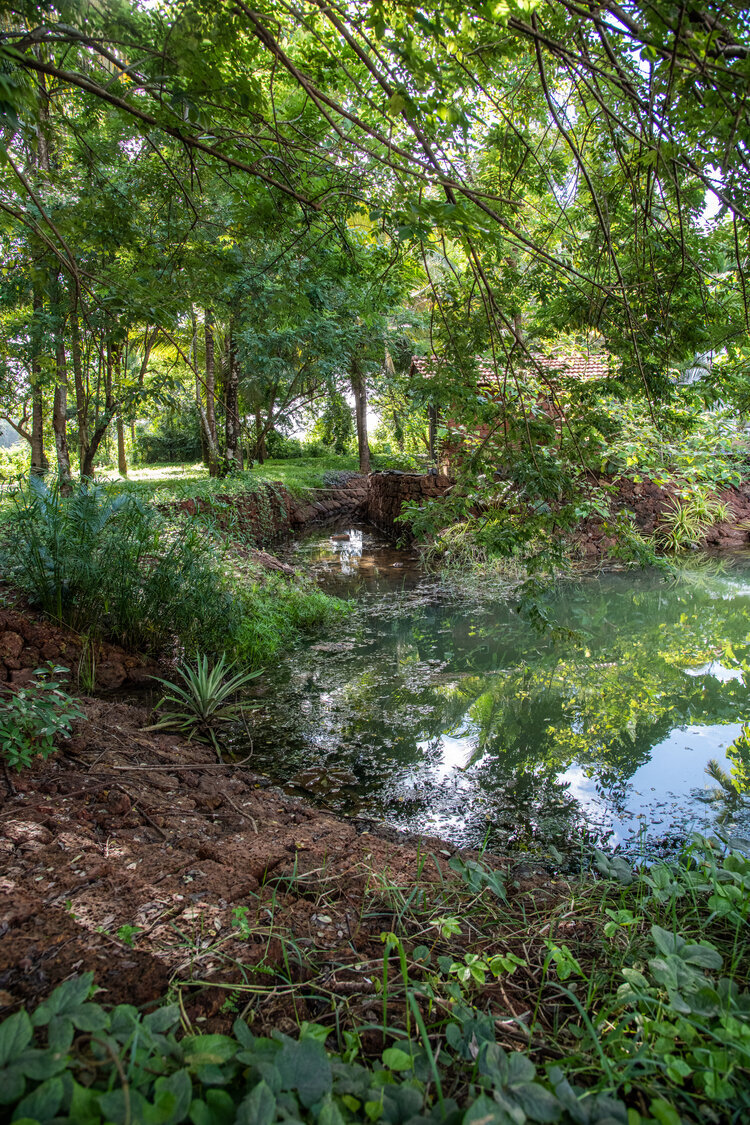
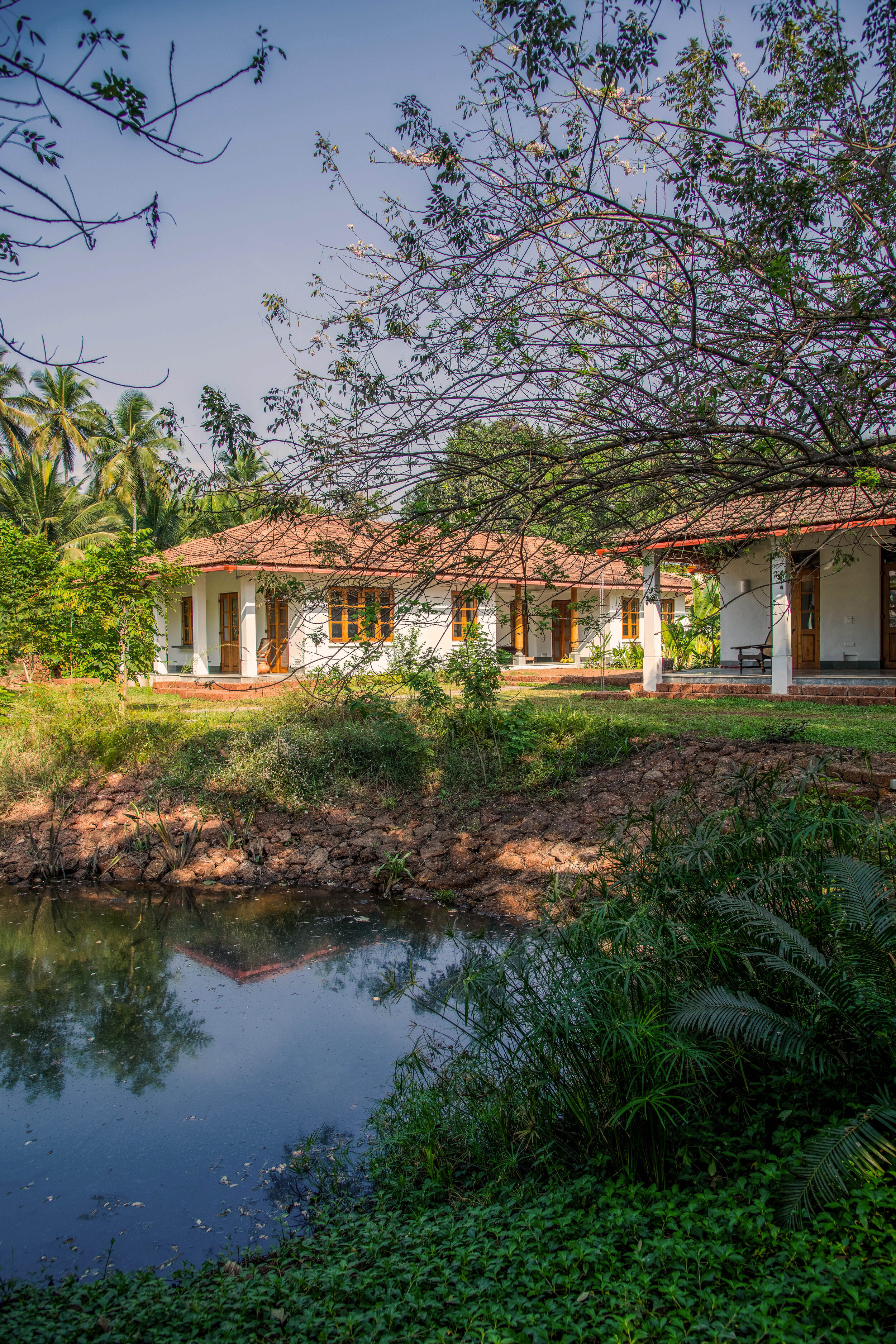
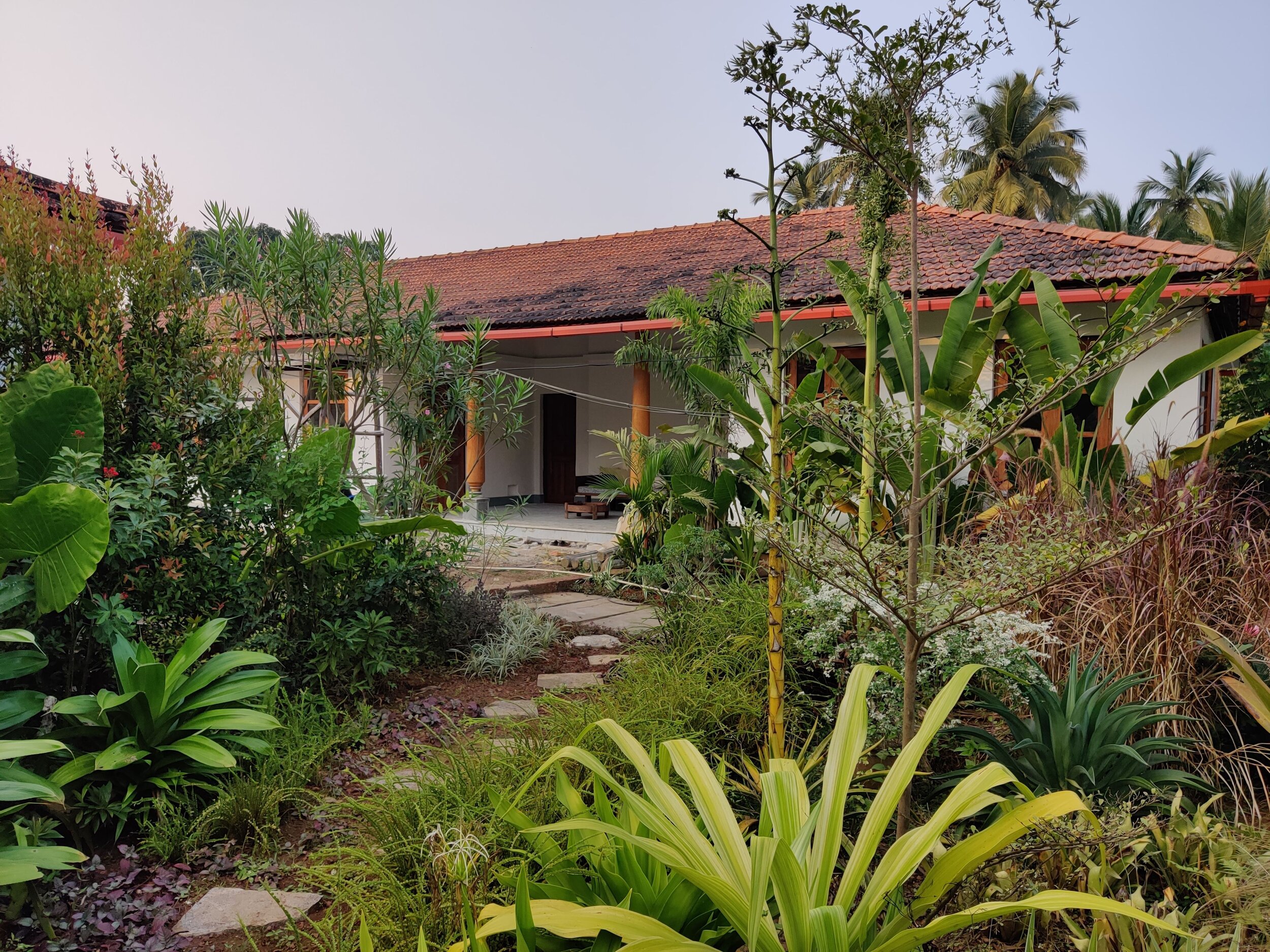
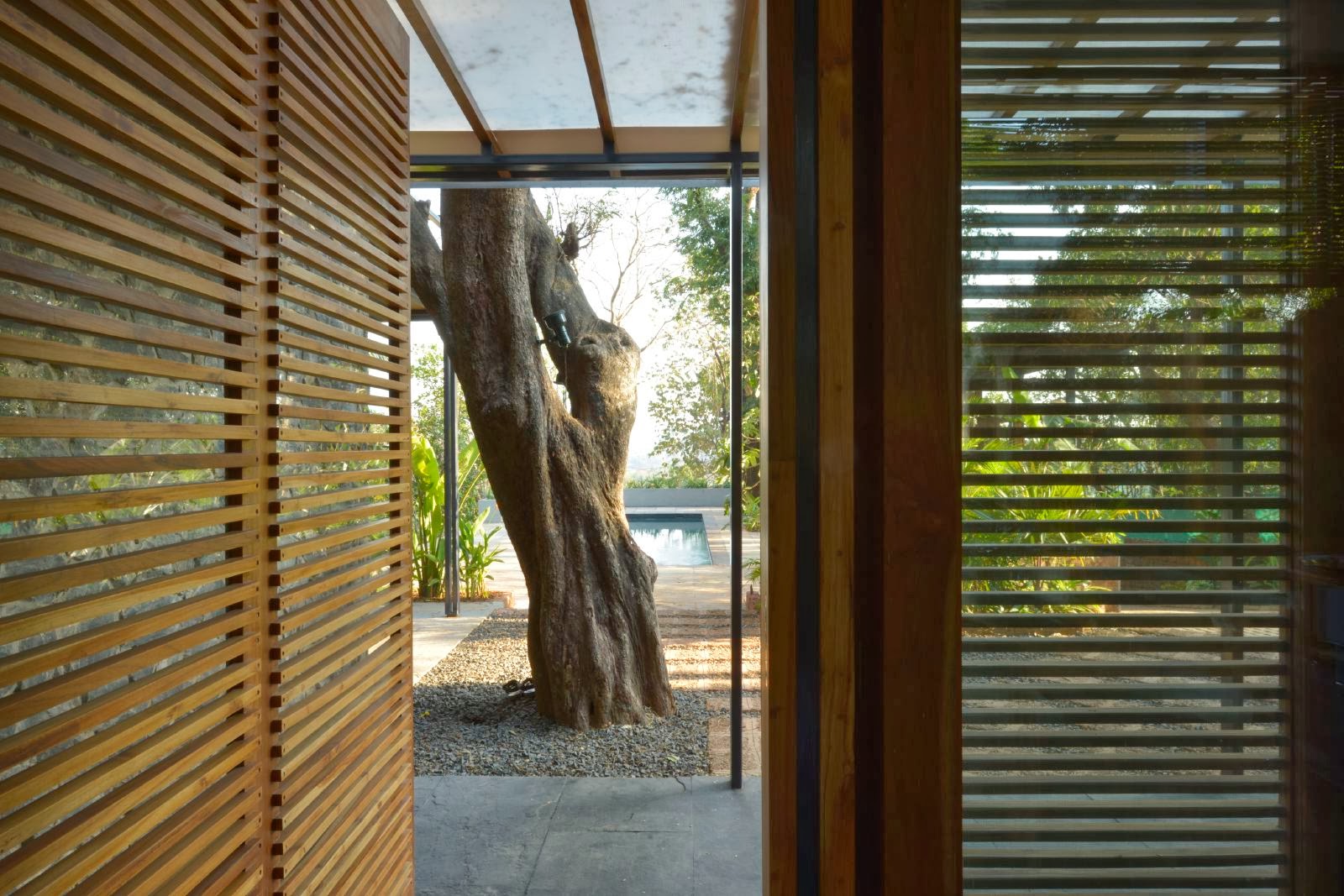
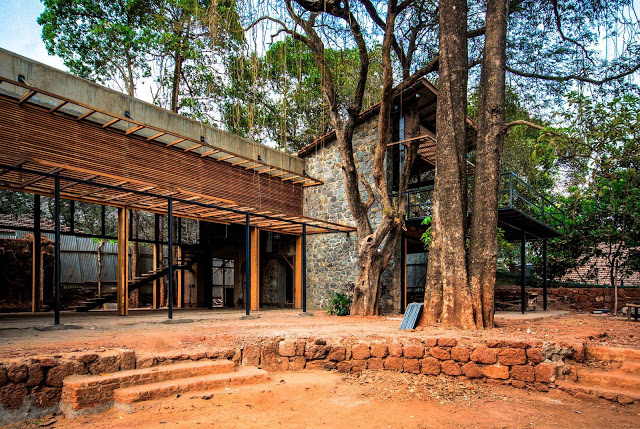
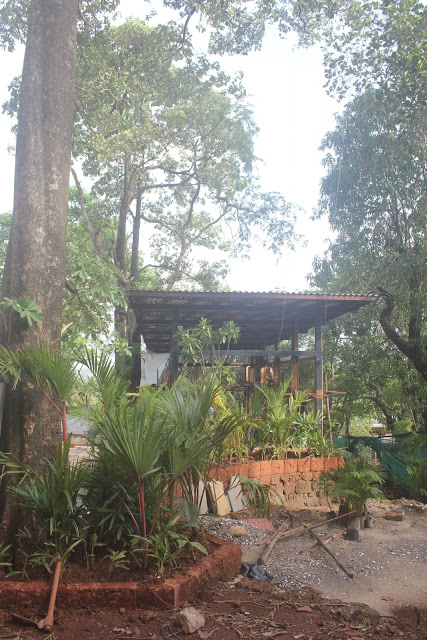
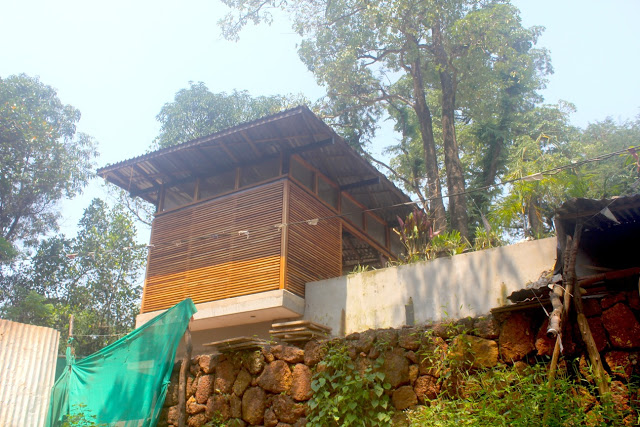
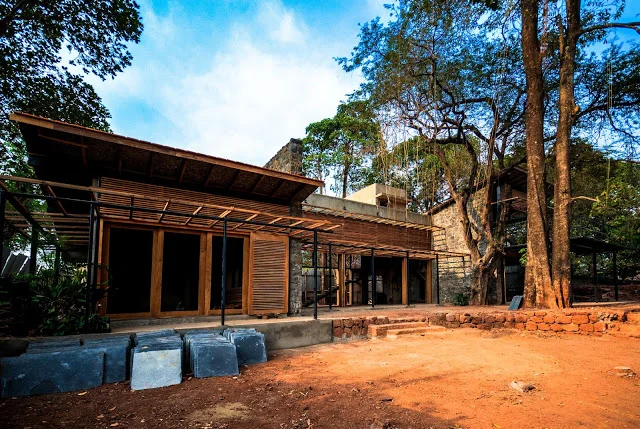
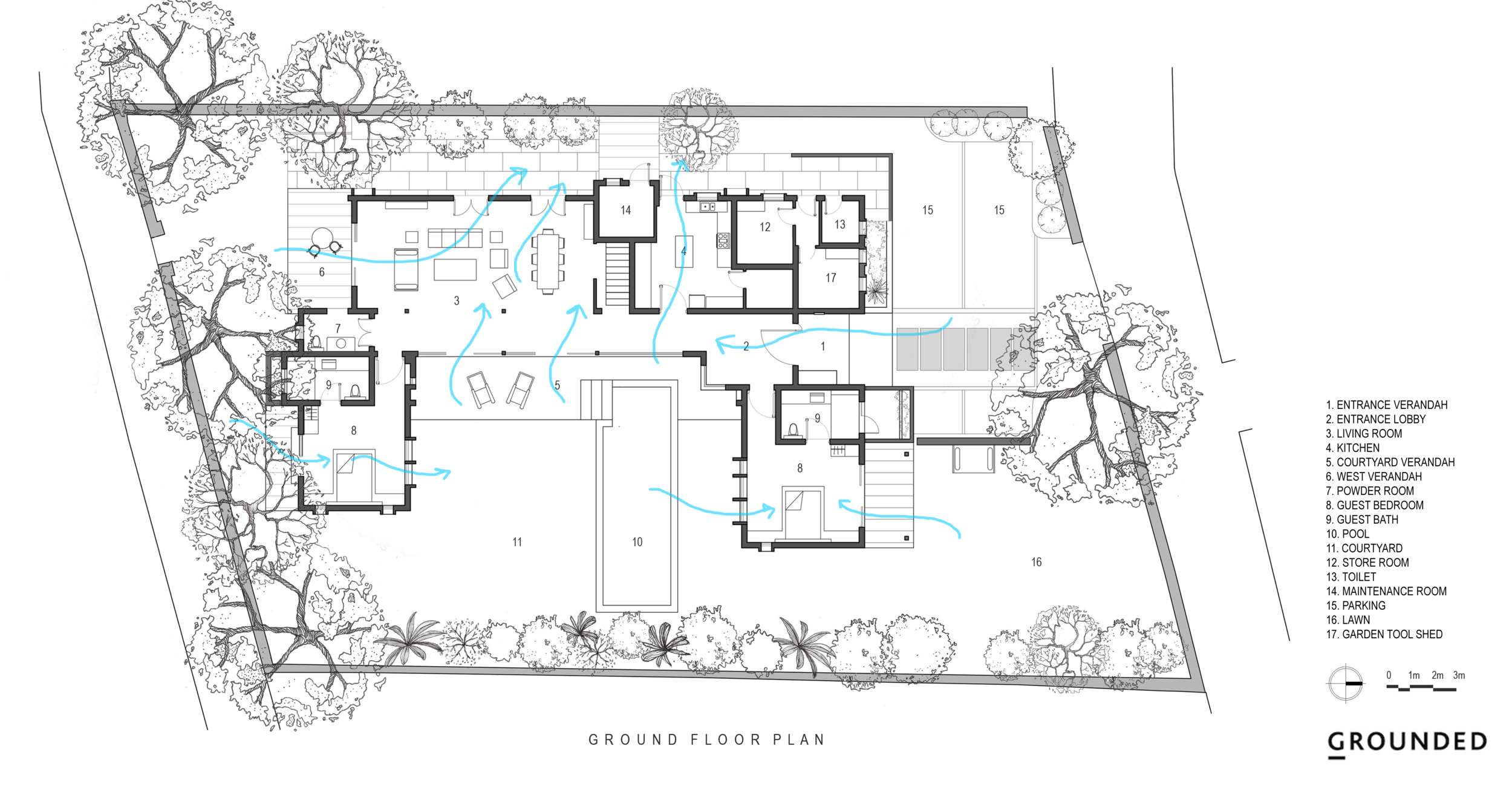
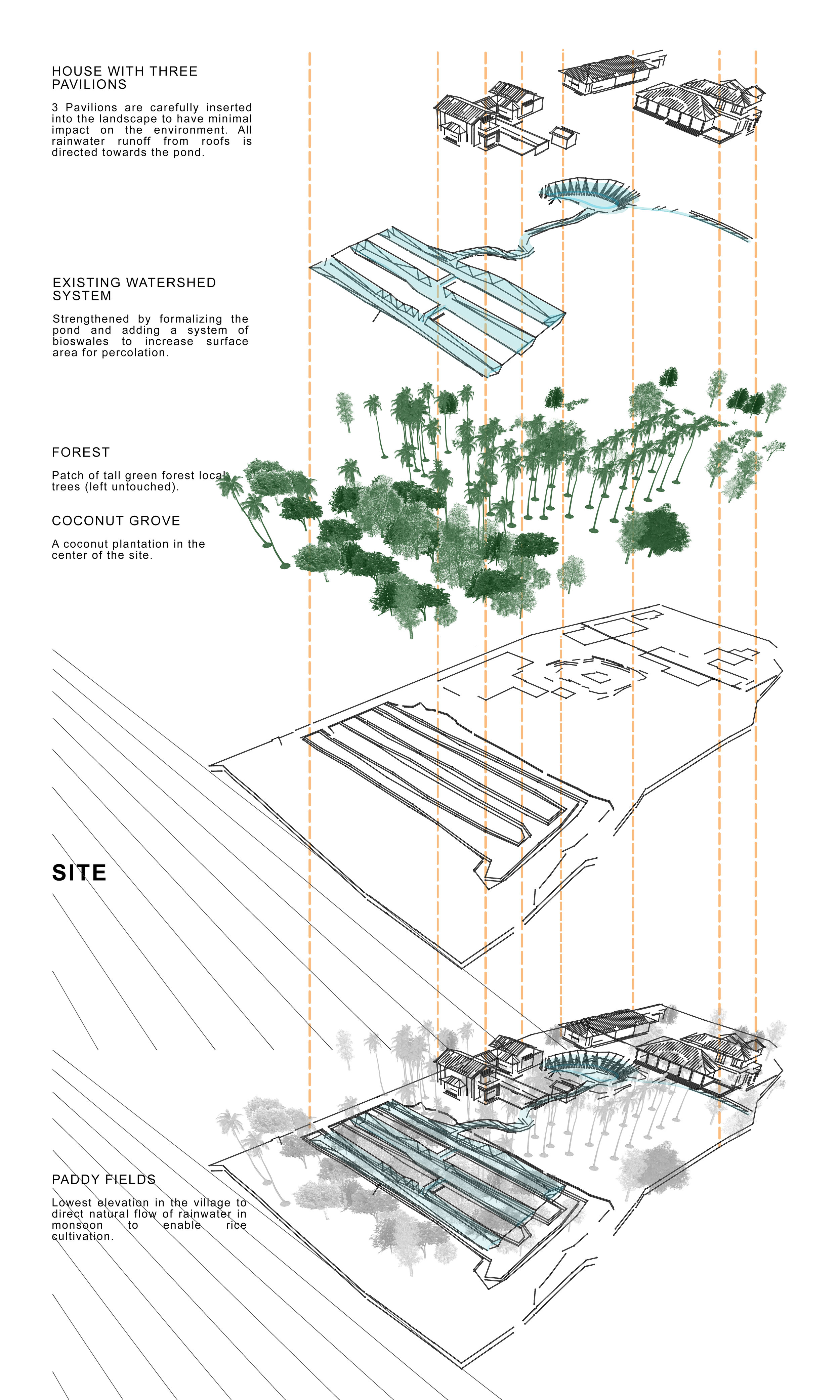
It is such a joy to see our project House with Three Pavilions find beautiful space in print and on the cover of Livingetc Magazine’s June 2022 issue. Aptly titled - ‘A Home with A Verandah’, the article draws attention to our countryside Goan house’s tangible connection to nature. It throws light on our tropical modern design approach and celebrates our efforts to create seamless indoor-outdoor spaces that allow our clients to take everyday life outdoors.
Read the published story here.
If you are considering buying a house in Goa, read our blogpost: What to Look For While Buying A House in Goa
To know more about our design process, take a look at: Designing A House in Goa

Grounded will soon be launching 2 new luxury villas for sale in North Goa. Like all our other residential projects, the villas will be sustainable, architecturally relevant, and closely connected to nature.
Register your interest using the link below to know more about the villas:
https://lnkd.in/dJfR9hS4
Celebrating the rustic yet contemporary nature of Utsav House by architect Bijoy Jain.
A simple, 5 step guide to design and build houses with rustic and luxurious spaces that are connected to nature.