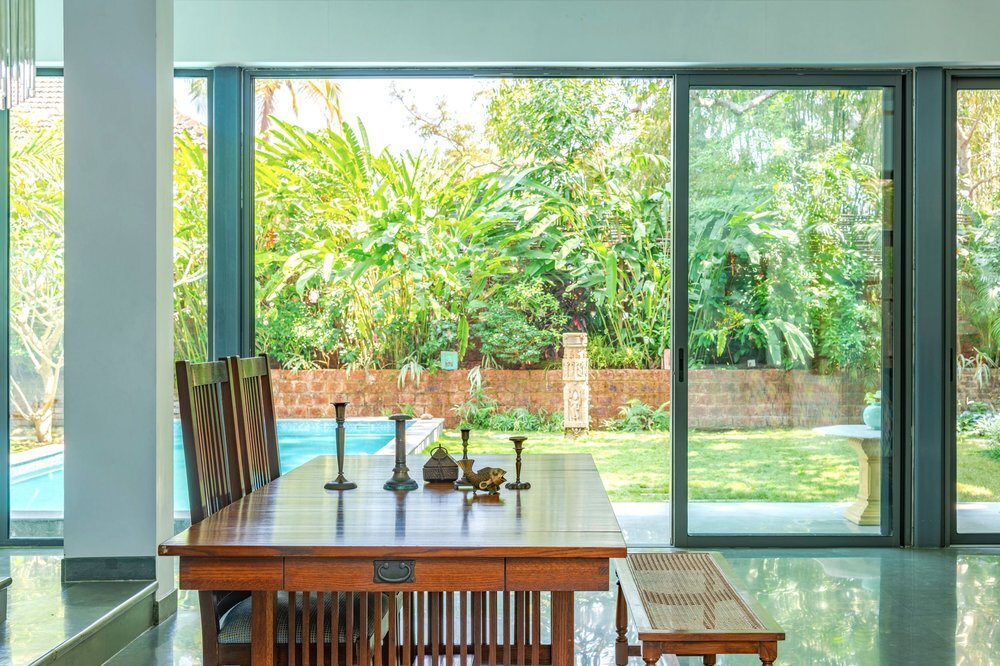
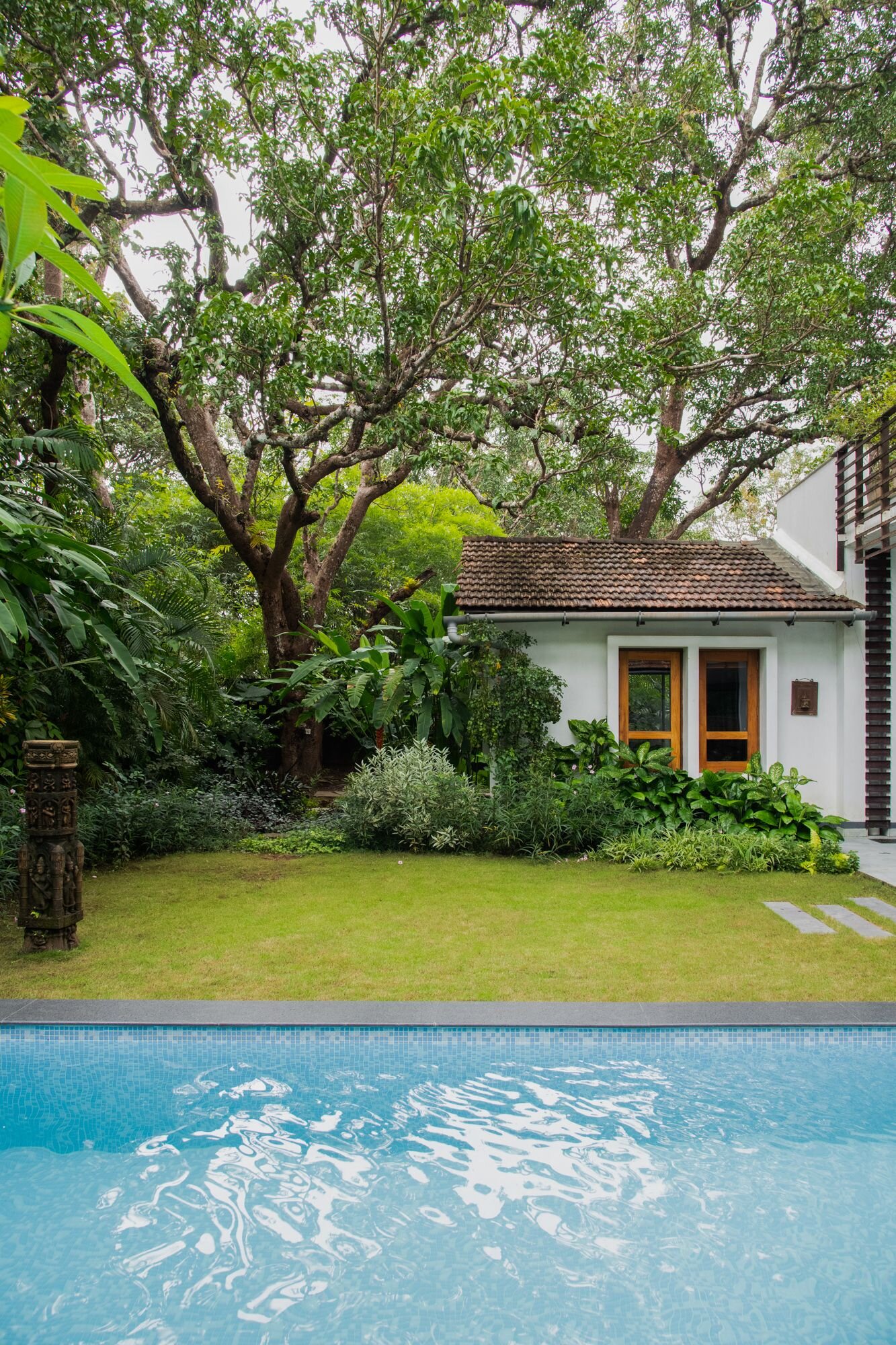
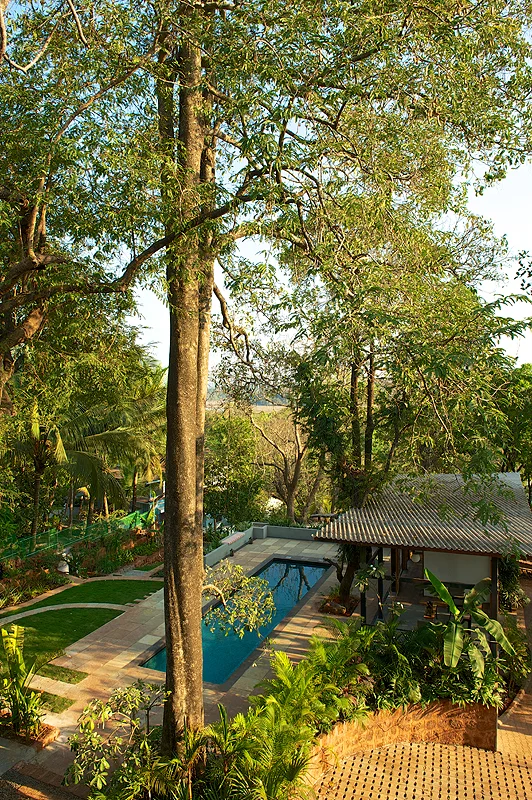
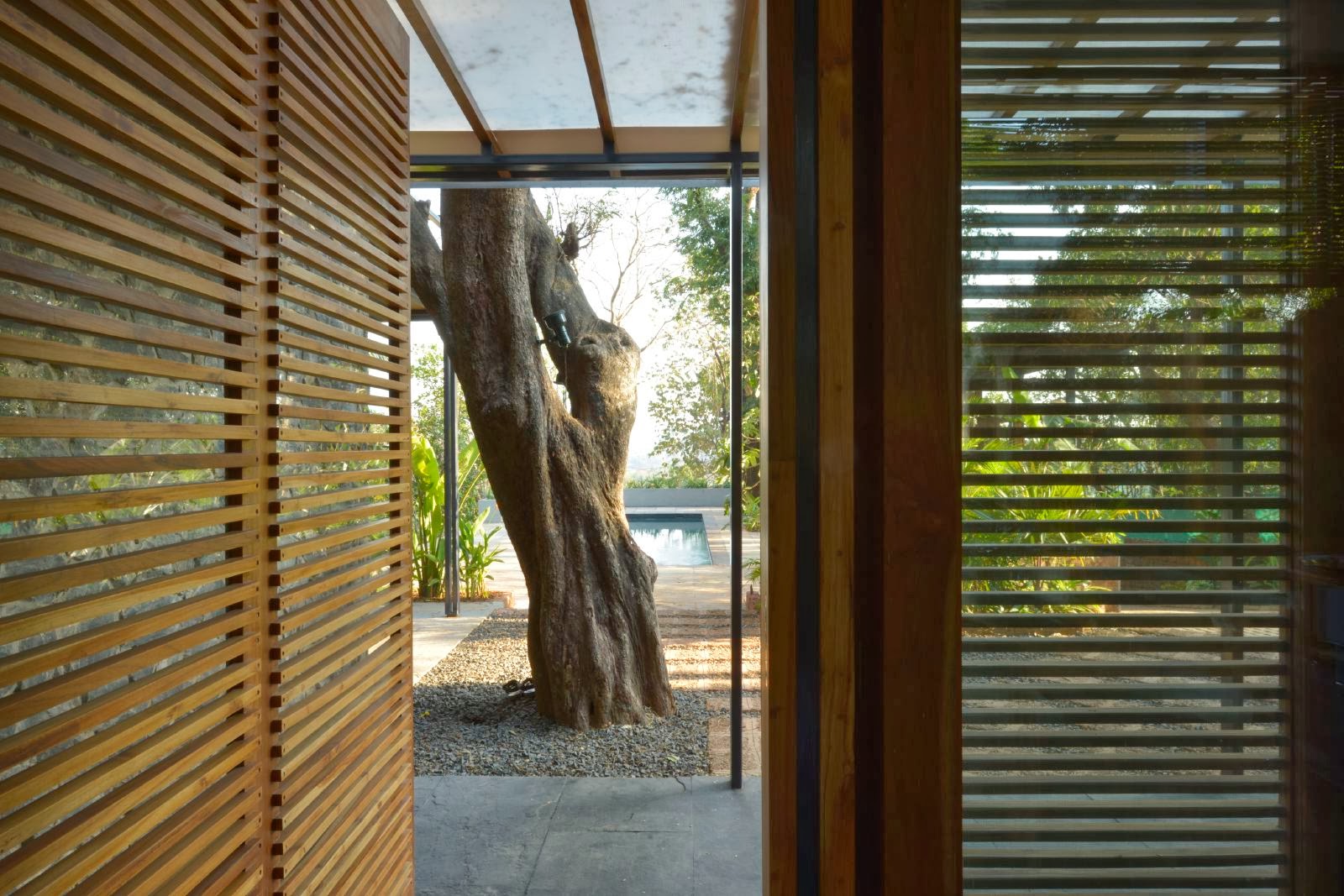
Geoffrey Bawa is an unforgettable and continuous inspiration. With every project we embark on, we see our inspiration translate into our work - in design, in spatial character, in connection and reverence towards nature - finding new meaning in every site we build on. Finding Bawa is a gallery we have compiled as an ode to the master architect. As we reflect on our projects, it feels great to see many of our spaces carrying the sensibilities and sensitivites that Bawa inspired throughout his practice.
Geoffrey Bawa was one of the original proponents of Tropical Modernism, a design movement in which sensitivity for local context combines with the form-making principles of modernism. His architecture led to the formation of a new architectural identity and aesthetic, redefining what it meant to be modern, celebrating a close connection with one’s built and natural environments.
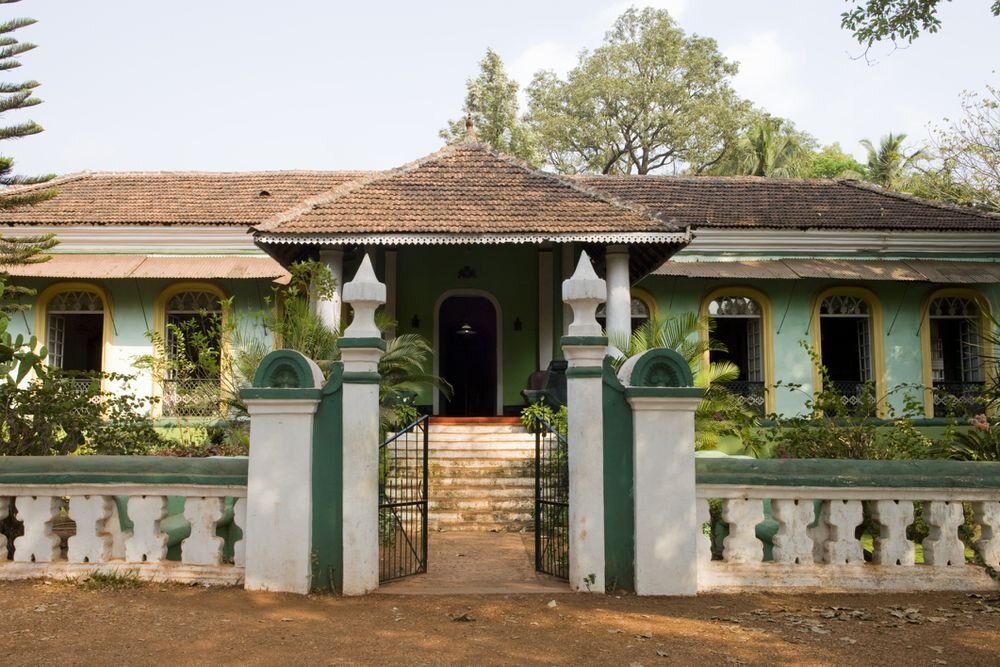
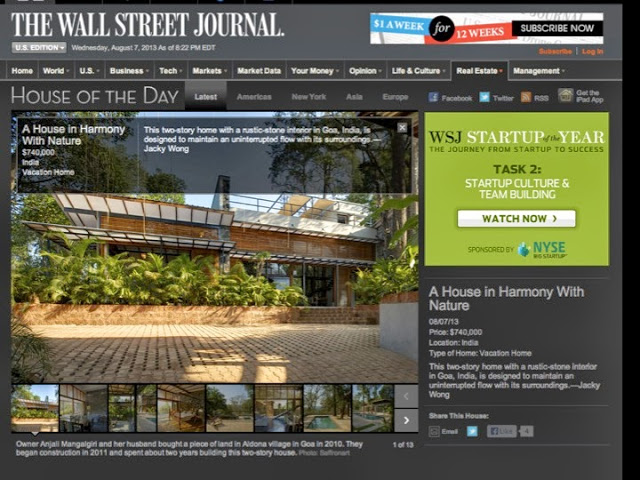
In 1960, Bawa was commissioned to design the house for artist Ena De Silva. Set in Colombo, the plot was very much enmeshed in the busy urban fabric with the activity and movement of any capital city.
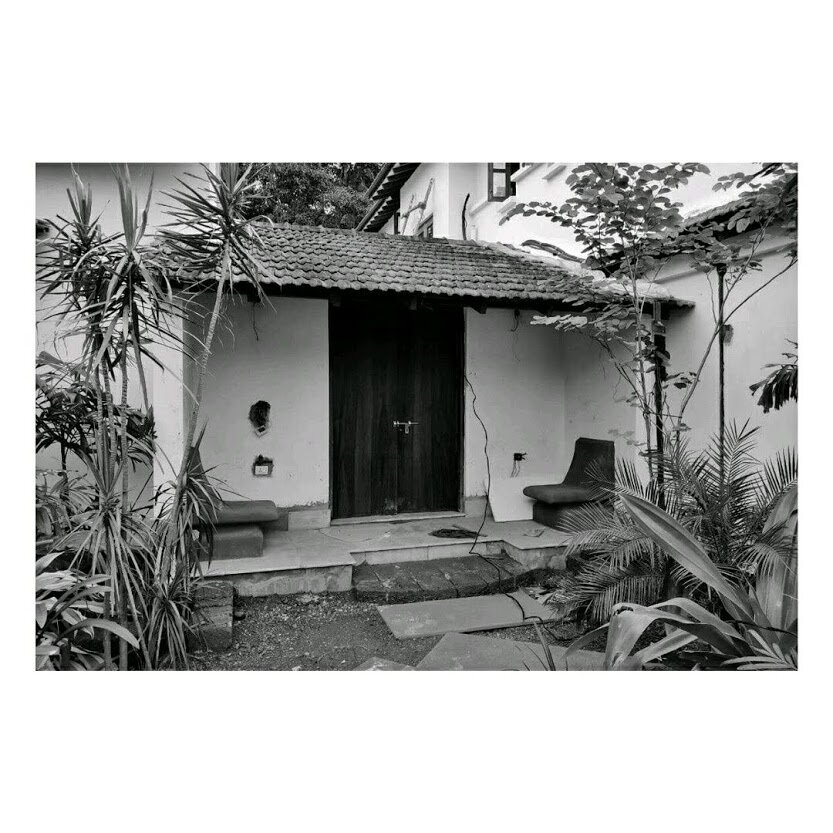
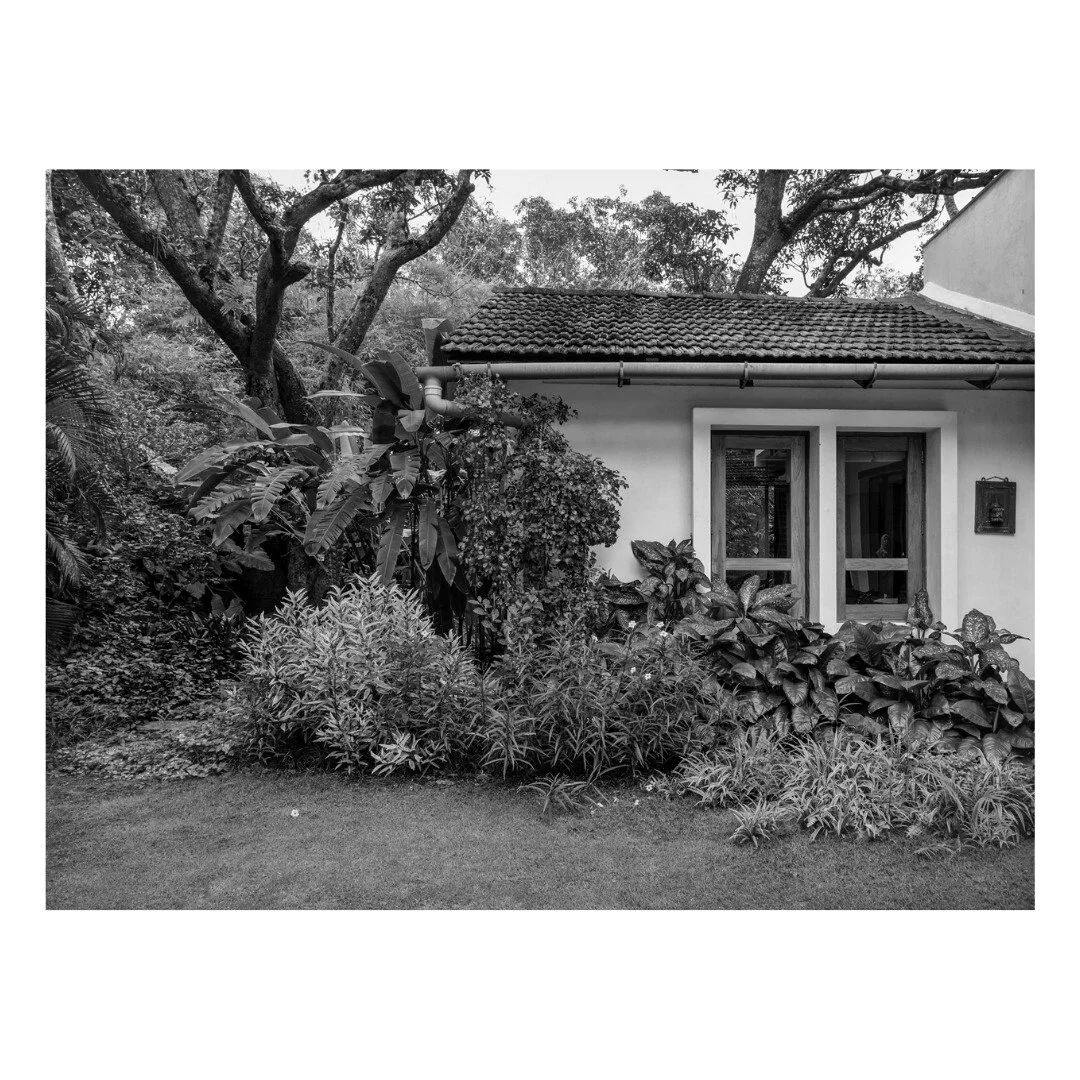
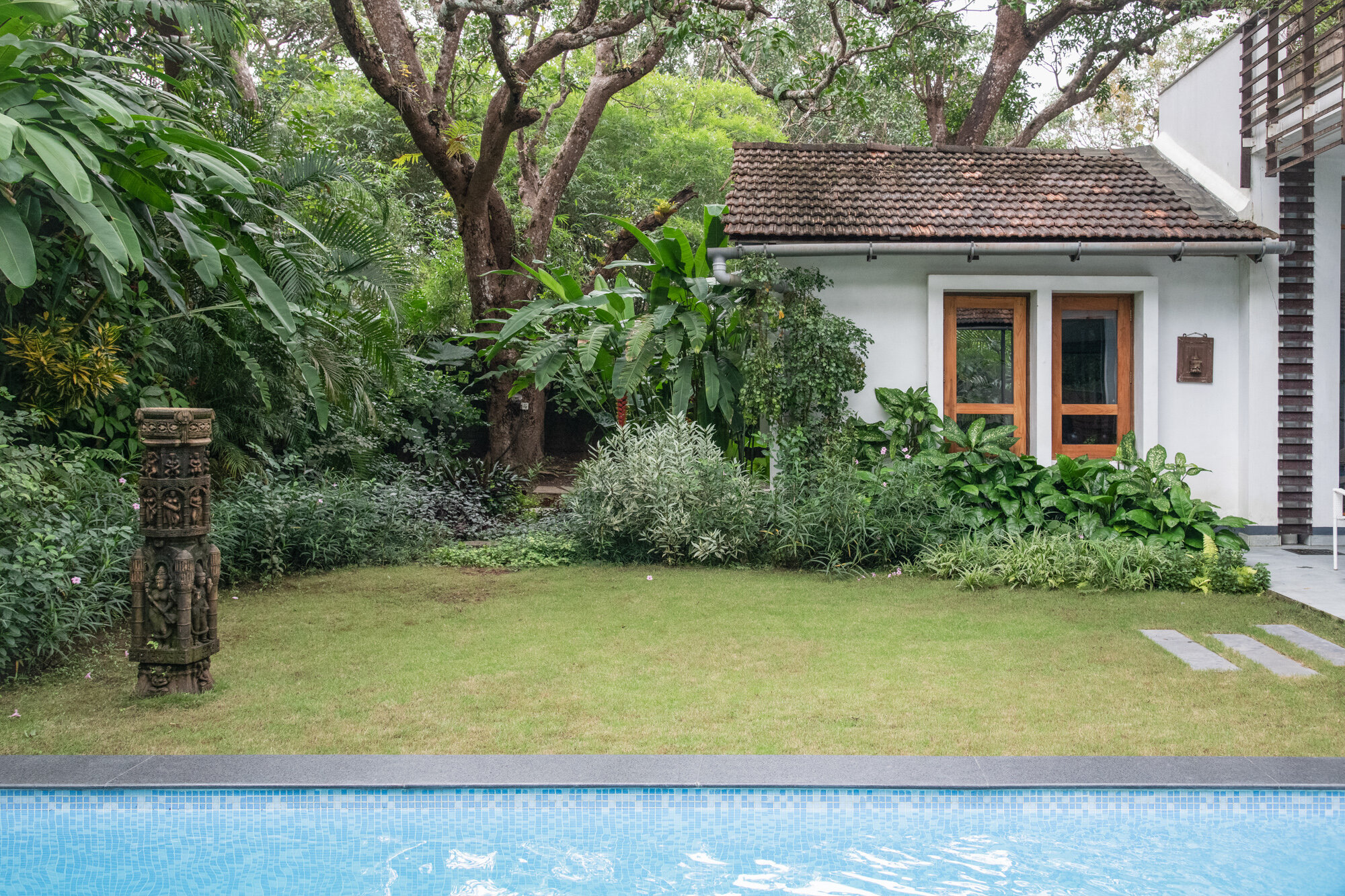
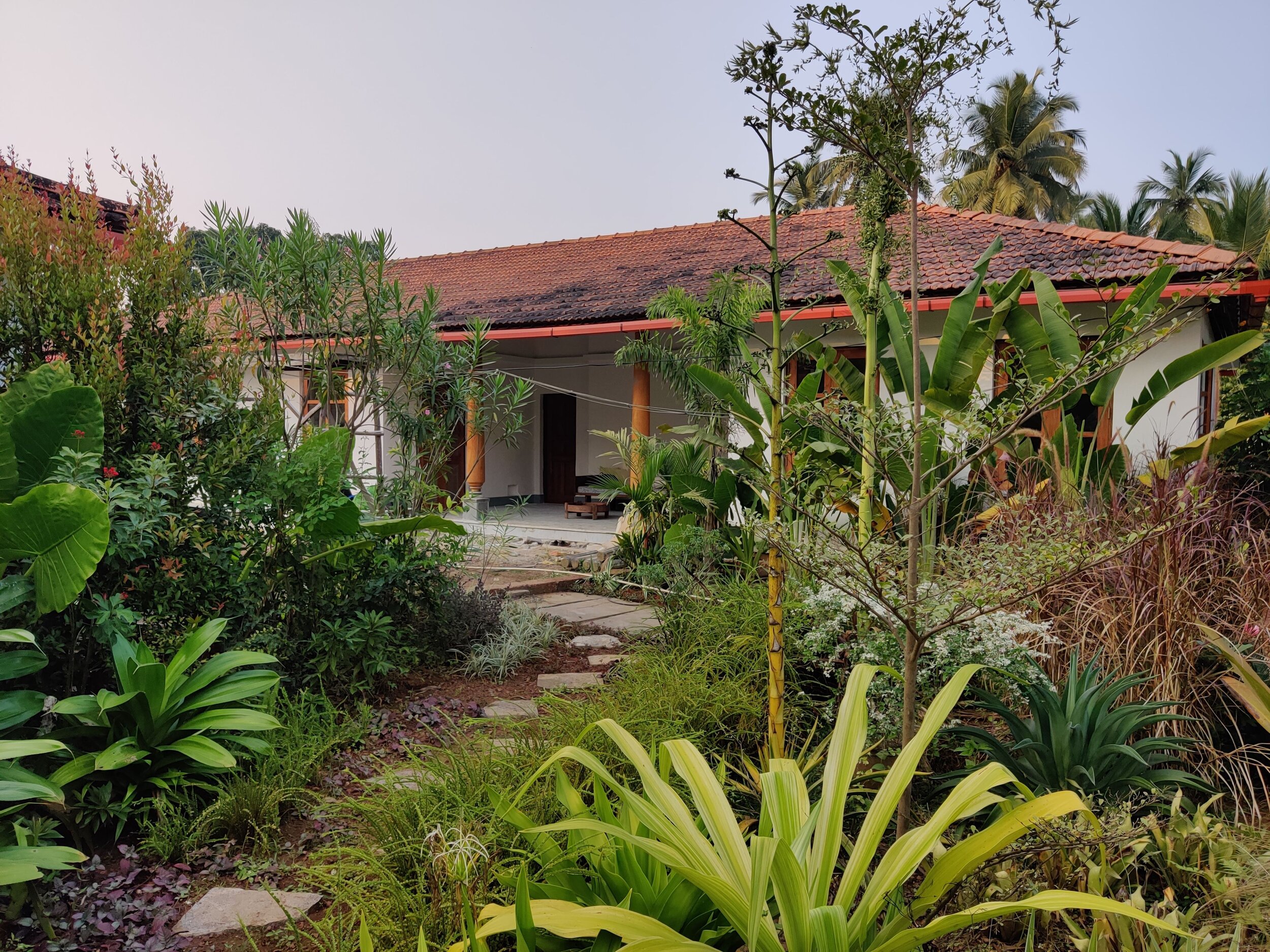
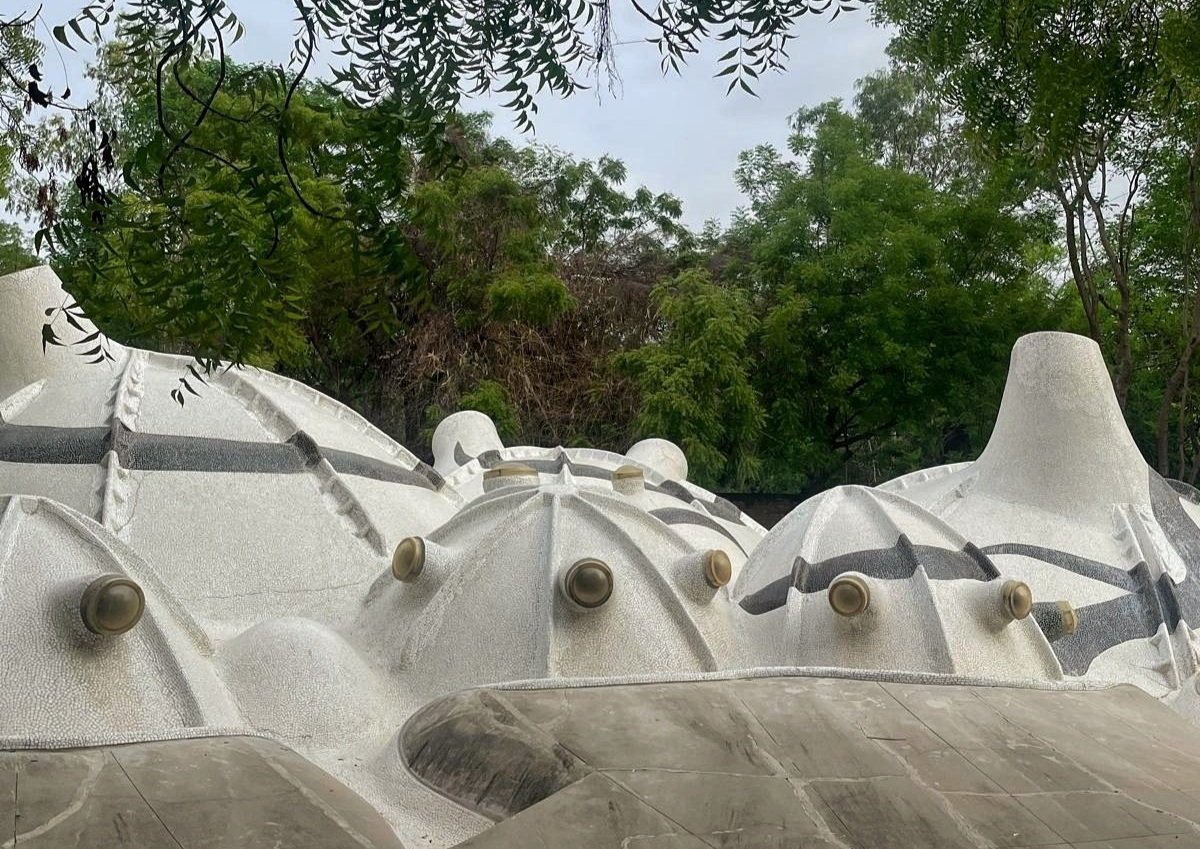
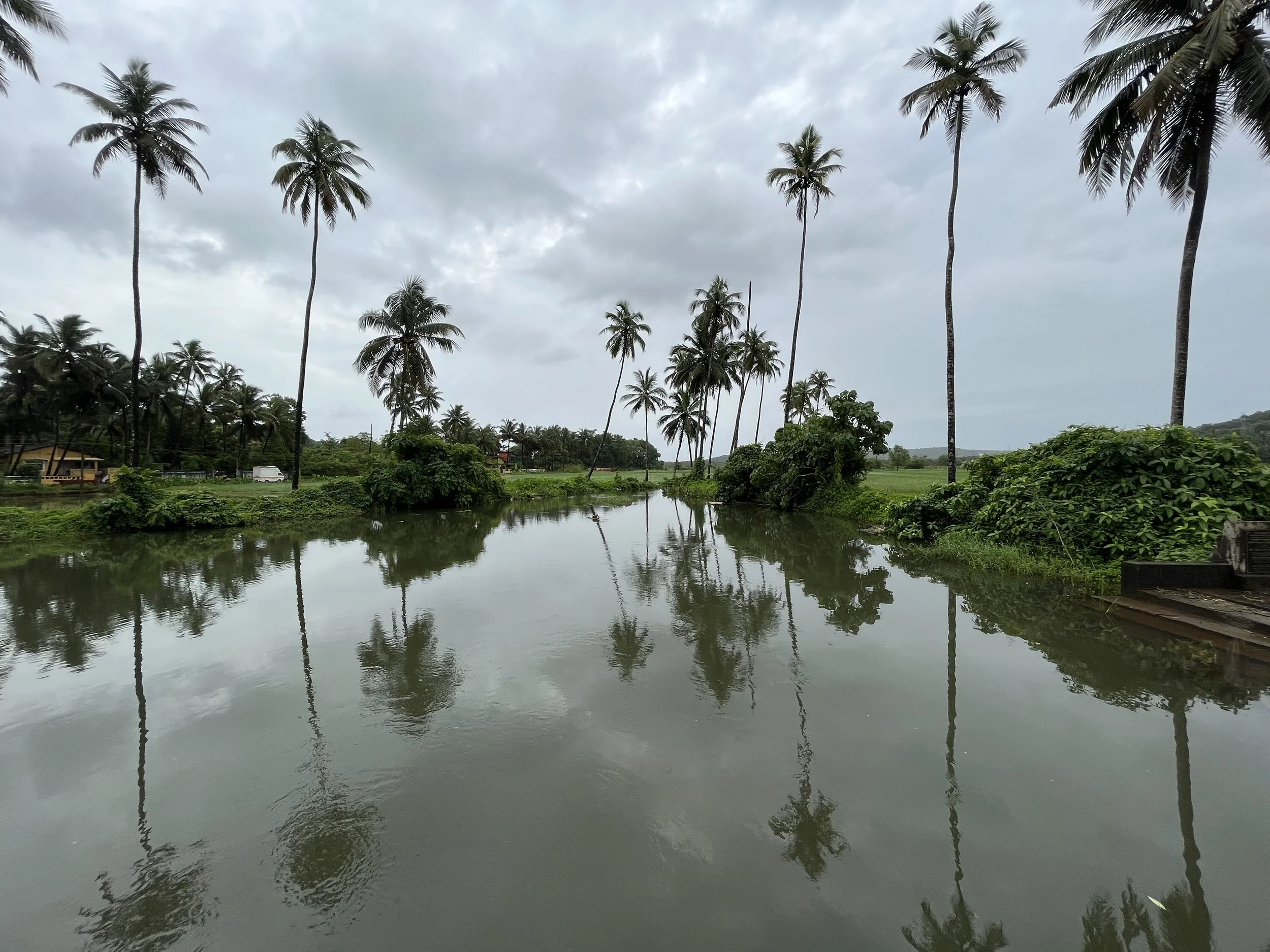
Bawa’s first response was to turn the house in on itself and resurrect the courtyard. The house was conceived as a series of pavilions and verandas contained within a high surrounding boundary wall. A major central courtyard led forward to five smaller satellite courtyards. Light and air poured into every room, with notions of inside and outside blurred nearly beyond distinction.
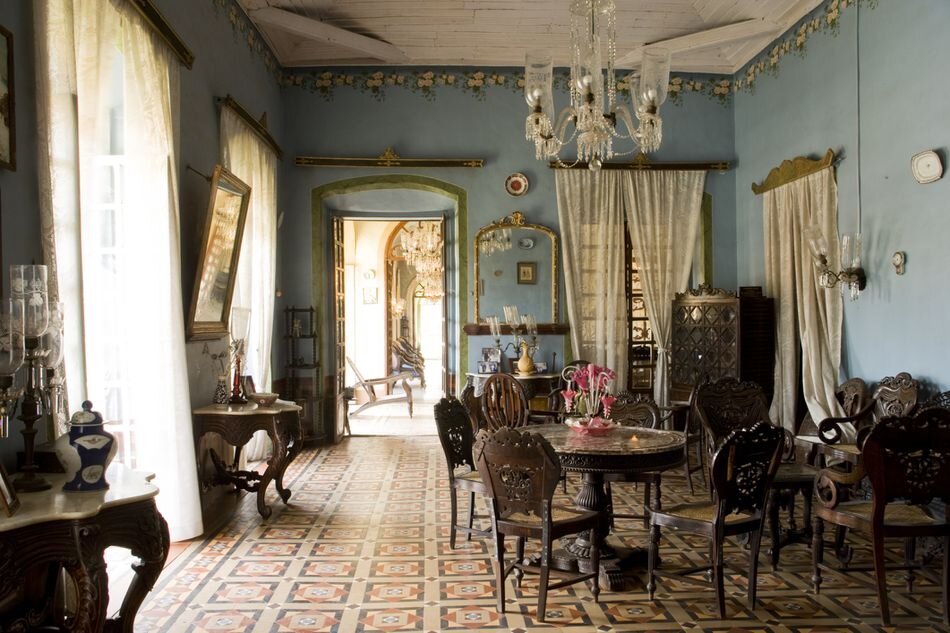
Its spatial qualities were enhanced by the choice of materials: walls of plastered brick, roofs of half-round Portuguese tiles, columns of satin wood, windows of timber lattice, floors of rough granite- materials that were used in ancient Sri Lankan mansions, but brought together in the contemporary open plan format, assembled in an entirely different manner.
After nearly 40 years of living here, Ena was finally forced to sell the house owing to health concerns and mounting bills. Her land in central Colombo was immensely valuable and was quickly snapped up by an adjoining hospital. But the idea of demolition was met by public outcry that made Urban Development Authority insist that the house must be preserved in its entirety.
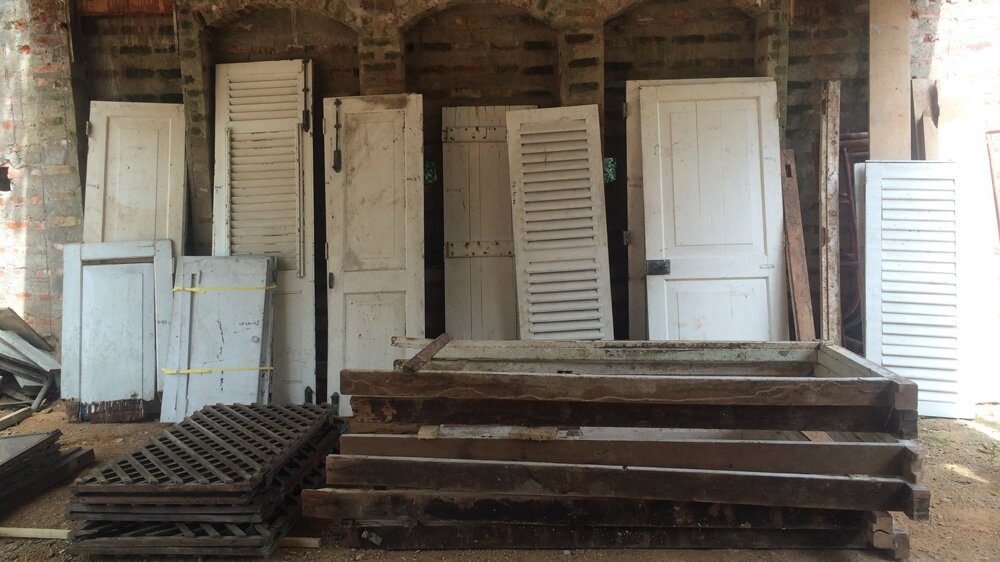
This is when the Bawa Trust proposed an unusual solution - to move the house in order to reconstruct it. A team of architects, archaeologists and development contractors came together, led by conservation specialist Nilan Cooray. Everything that could be salvaged from Ena de Silva’s home, including the doors and windows, was carefully collected, stored, and moved.
Unlike examples from Japan and Norway, where timber structures had been relocated successfully, Cooray had to work with masonry, some of which was falling apart. The house was stripped down to its bones - every pebble in the courtyard was numbered, every shape was traced, before he was done. They paid particular attention to replicating the structure’s orientation to the Sun, because that was essential to Bawa’s original palette of light and shadow. Working from the roof down, they dismantled the house, which was boxed up and loaded on to lorries to be carted off to a plot next door to Lunuganga, Bawa’s beautiful garden home.
The process took six years from start to finish, and the Ena De Silva house was finally assembled to completion in its new home in 2016.
Relying on black and white photos and surviving furniture, the Bawa Trust intends to return Ena’s house to a spitting image of how she had kept it, even replanting the garden with her choice of plants. It takes the spirit and act of conservation to uncharted territory, preserving Bawa’s legacy for generations to come.